Achtergrond
Het INCA model is een referentie integraal zorgprogramma dat het maken van integrale Individuele
Zorgplannen (IZP) conform zorgstandaarden faciliteert. En in het verlengde daarvan ook de organisatie en
integrale bekostiging voor de (sub)populatie. Het model speelt in op de uitdagingen die de implementatie
van het IZP op geleide van de specifieke patiëntbehoeften bemoeilijken: De heterogeniteit binnen de
populatie, co- en multimorbiditeit, de problematiek van het samen beslissen en het ontbreken van
eenheid van taal tussen zorgverleners en zorgverzekeraars.
De essentie van het INCA model is om in het primaire proces, de productieve interacties tussen cliënt en
zorgverleners, te ondersteunen. Informatie uit het consult en wat reeds bekend is in het dossier wordt
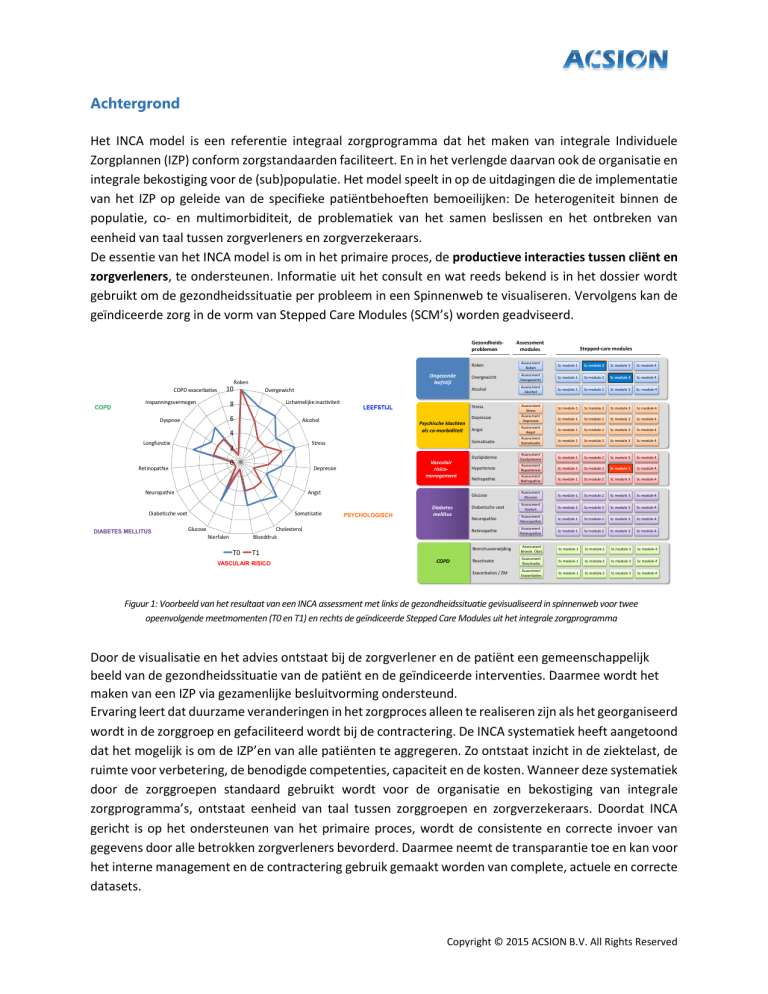
gebruikt om de gezondheidssituatie per probleem in een Spinnenweb te visualiseren. Vervolgens kan de
geïndiceerde zorg in de vorm van Stepped Care Modules (SCM’s) worden geadviseerd.
Gezondheidsproblemen
Ongezonde
leefstijl
Roken
COPD exacerbaties
COPD
10
Inspanningsvermogen
8
Dyspnoe
6
Overgewicht
Lichamelijke inactiviteit
LEEFSTIJL
Psychische klachten
als co-morbiditeit
4
Longfunctie
Stress
2
0
Retinopathie
Neuropathie
Angst
Diabetische voet
DIABETES MELLITUS
Vasculair
risicomanagement
Depressie
Somatisatie
Glucose
PSYCHOLOGISCH
Diabetes
mellitus
Cholesterol
Bloeddruk
Nierfalen
T0
T1
VASCULAIR RISICO
COPD
Stepped-care modules
Roken
Assessment
Roken
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Overgewicht
Assessment
Overgewicht
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Alcohol
Assessment
Alcohol
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Stress
Assessment
Stress
Assessment
Depressie
Depressie
Alcohol
Assessment
modules
Sc module 4
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Angst
Assessment
Angst
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Somatisatie
Assessment
Somatisatie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Dyslipidemie
Assessment
Dyslipidemie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Hypertensie
Assessment
Hypertensie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Nefropathie
Assessment
Nefropathie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Glucose
Assessment
Glucose
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Diabetische voet
Assessment
Voeten
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Neuropathie
Assessment
Neuropathie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Retinopathie
Assessment
Retinopathie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Bronchusverwijding
Assessment
Bronch. Obst.
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Reactivatie
Assessment
Reactivatie
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Exacerbaties / ZM
Assessment
Exacerbaties
Sc module 1
Sc module 2
Sc module 3
Sc module 4
Figuur 1: Voorbeeld van het resultaat van een INCA assessment met links de gezondheidssituatie gevisualiseerd in spinnenweb voor twee
opeenvolgende meetmomenten (T0 en T1) en rechts de geïndiceerde Stepped Care Modules uit het integrale zorgprogramma
Door de visualisatie en het advies ontstaat bij de zorgverlener en de patiënt een gemeenschappelijk
beeld van de gezondheidssituatie van de patiënt en de geïndiceerde interventies. Daarmee wordt het
maken van een IZP via gezamenlijke besluitvorming ondersteund.
Ervaring leert dat duurzame veranderingen in het zorgproces alleen te realiseren zijn als het georganiseerd
wordt in de zorggroep en gefaciliteerd wordt bij de contractering. De INCA systematiek heeft aangetoond
dat het mogelijk is om de IZP’en van alle patiënten te aggregeren. Zo ontstaat inzicht in de ziektelast, de
ruimte voor verbetering, de benodigde competenties, capaciteit en de kosten. Wanneer deze systematiek
door de zorggroepen standaard gebruikt wordt voor de organisatie en bekostiging van integrale
zorgprogramma’s, ontstaat eenheid van taal tussen zorggroepen en zorgverzekeraars. Doordat INCA
gericht is op het ondersteunen van het primaire proces, wordt de consistente en correcte invoer van
gegevens door alle betrokken zorgverleners bevorderd. Daarmee neemt de transparantie toe en kan voor
het interne management en de contractering gebruik gemaakt worden van complete, actuele en correcte
datasets.
Copyright © 2015 ACSION B.V. All Rights Reserved
Figuur 2: Schematische weergave van de wijze waarop de INCA systematiek de gezamenlijke besluitvorming t.b.v. een IZP, het intern
management en de contractering ondersteunt.
Advantages of INCA
For the patient
The holistic approach and tailoring of care to the specific needs of patients in a validated manner helps to
assure patients are taken care of based on their specific needs in life and in relation to their disease. The
major advantage for them is that they feel understood and in course of time their quality of life is
maintained.
Individual caregivers
The GP and specialized nurse have a validated instrument to support Shared Decision Making with their
patients and to motivate them to be committed and to comply with the needs of their disease and life.
They can also visualize the results of their efforts with this patient population. Furthermore the
multidisciplinary team members have the right information at the right moment.
For internal management of healthcare groups and population management
Since all data and choices are electronically registered the total of all individual care profiles can easily be
aggregated. This provides an accurate picture of the case mix and the nature and volume of the care to
be delivered by a healthcare group based on the actual health needs of their chronically ill population.
Copyright © 2015 ACSION B.V. All Rights Reserved
This offers great advantages. For example you can determine the actual health problems in a population.
You can also identify the room for improvement in the health status of that population, which care should
be provided and what competencies (healthcare professionals) have to be procured to deliver this care.
Hence multidisciplinary healthcare groups can manage their organization, processes, quality and financing
based on the aggregated individual profiles.
Payers
Most important for payers is that the care delivered was indicated and necessary. If not, they pay for
unnecessary care. The fact that the care to be delivered is assessed bottom up in the individual care
process and then aggregated to population level ensures that appropriate care is provided and procured.
The costs for medication, laboratory tests and referrals are mainly driven by chronic diseases like diabetes
and cardiovascular diseases. It is to be expected that part of these expenses is waste because of
unnecessary prescription, lab test and referrals. This can be avoided when the care is coordinated and
registered electronically. Moreover, when these patients are taken care of structurally, costly
complications, such as myocardial infarction, dialysis and amputations as well as hospitalizations can be
avoided.
Furthermore, uniformity in chronic care programs from different care providers is desirable for decision
making in the procurement process. Otherwise payers have to assess the programs every time again.
Governments
Optimal care is delivered, waste is avoided and a clear morbidity and care needs registration. Based on
the latter capacity can be planned on a regional or national level.
Current status of the INCA model
The development of the INCA model is going into its 3rd phase:
1. Phase 1: Development of the Assessment and Stepped Care Modules (2010-2012)
2. Phase 2: Pilots to test model with retrospective data of care practices (2013-2014)
3. Prospective pilots with the INCA model in real patient care in 4 care groups
So far INCA has been received enthusiastically by patients, their care providers, care group managers and
health insurers. Reason why they want to test the model further and tailor it for widespread use.
Copyright © 2015 ACSION B.V. All Rights Reserved