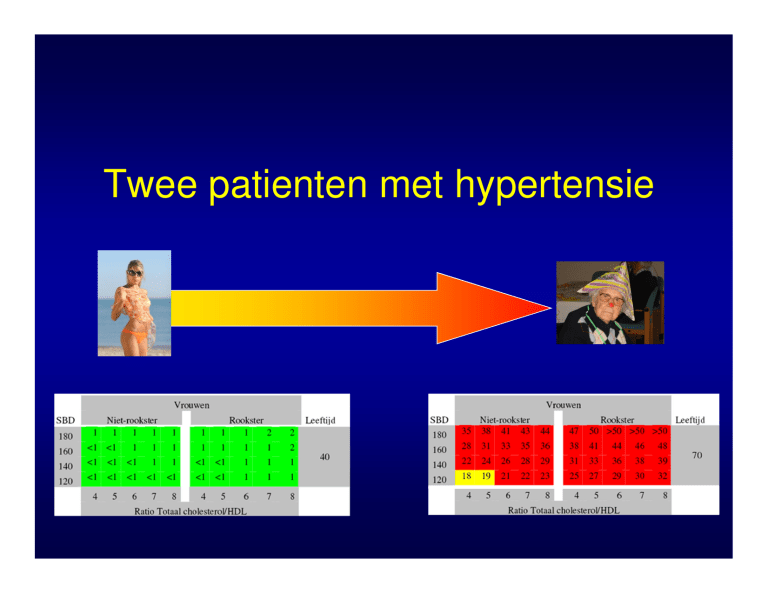
Twee patienten met hypertensie
‘De patient met hypertensie’
Normaal, compliant
vaatstelsel
Arteriele stijfheid,
Athero/arteriolosclerose
Laag risico op HVZ
Hoog risico op HVZ
Behandeling?
Behandeling, maar niet
perse op streefwaarde
Look for cause
Look for effect
RAS dependent
‘hoog renine HT’
Volume dependent
‘laag renine HT’
Een jonge patient met hypertensie
42 jarige vrouw verwezen met hypertensie 165/105 mmHg
Laatste tijd vaak hoofdpijn, ‘gejaagd’. Rookt 5 sig dd
FA: HT + bij moeder ~40 jr, 1 zus bij nefroloog (reden?)
Med: oraal anticonceptivum
Intox: spor. drop, verder -
LO: Nl., BMI 28, BP 172/106 li ~ re, pols 92 r/a, art. fem. palp.
Lab.: K 3.6 mmol/l, kreat 76 umol/l
Urine: microalb./kreat 13.5 mg/mmol
ECG: geen LVH
Een patient met hypertensie
Hypertensie (symptomatisch ?) met microalbuminurie bij
overgewicht en positieve familie-anamnese
Differentiaal diagnose ?
Essentieel
Anticonceptiepil
Parenchymateuze nierziekte
Hyperthyreoidie
Primair hyperaldosteronisme
Feochromocytoom
Renovasculair
Coarctatio
Essentiele hypertensie: 2 + 2
Multifactoriele aandoening veroorzaakt door:
I. complex genetische predispositie (enkele zeldzame
monogenetische varianten)
+
II. omgevingsfactoren (calorieën/zout, stress, alcohol,...)
III. leeftijdsgerelateerde toename vaatwandstijfheid
+
IV. afname aantal nefronen
Bloeddruk en overgewicht
Wild, S. H et al. BMJ 2006;333:1009-1011
Anticonceptiepil
•
•
•
•
•
•
OAC: ∆ bloeddruk +6/3 mmHg
±1% matig-ernstige HT; na maanden/ jaren
RR op HT: 1.8 (1.5-2.3)
oestrogenen: ↑ angiotensinogeen in de lever
stoppen OAC: effect op bloeddruk na 3 mnd weg
progestagenen alleen, Mirena spiraal
Nurses Health Study, Circulation
1996;94:483-489
Hyper & hypothyreoidie
•
Hypothyreoidie
- odds ratio HT 2.5-3.0
- prevalentie 3% polikliniek
- in normale range geen associatie
tussen THS en bloeddruk
•
Hyperthyreoidie
- associatie T3 ~ afw. HD circulatie
- systolische HT bij jonge pnten
Streeten, Hypertension 1988: 78
Hyper & hypothyreoidie
Circulation 2007:1725
Vervolg casus
Wat zou je doen ?
Oraal anticonceptivum stop
Sediment: geen afw.
Echo-nieren: normale vorm en grootte van de nieren bdz.
Lab: TSH 1.0 mE/l
feo-diagnostiek ?
Na 2 maanden: bloeddruk 168/102 mmHg
Verdere diagnostiek ?
Wie komt in aanmerking voor verder
onderzoek naar sec. oorzaken ?
1. potentieel diagnostische clue (PDC) uit
anamnese, lich. ond., standaard lab. onderzoek
2. therapieresistente of maligne hypertensie
3. jonge patienten (<30 jr) met HT zonder duid.
aanwijsbare oorzaak (obesitas, belaste FA HT*)
* bij sterk positieve FA voor HT op jonge leeftijd
denk aan zeldzame genetische vormen
Kans op genezing
Trinquart L, Hypertension 2010
Outcome of APA following surgery:
Age < 44 jr OR 6.2 for cure vs Age ≥ 44 jr
Celen O, Arch Surgery 1996
Kans op iets bijzonders
Bij FA ++:
PRA, aldosteron
Bij FA - + 0 clues:
EAI
directe angiografie
Vervolg casus
N<0.6 nmol/L
N<3.26 umol/24 uur
Blood vessel
DHPG 98%
7% NE 93%
NE
COMT
NE
NMN
40% NMN 60%
16%
NE
DHPG
44%
EPI
MN
90% MN 10%
COMT
Adrenal
medulla
99% EPI
Extraneuronal
Sympathetic
neuron
Klinische verdenking
24-uurs urine metanefrines
of plasma metanefrines
Indien normaal
tumor uitgesloten
< 4x stijging v. bovengrens
tumor mogelijk
Sterke stijging
>4 x v. bovengrens
tumor waarschijnlijk
herhalen plasma of urine
metanefrines
normaal
tumor uitgesloten
Metanefrines blijven verhoogd
Clonidinetest
Supressie van NA (of NMN)
tumor uitgesloten
Geen supressie van NA (of NMN)
tumor waarschijnlijk
Beeldvorming
Screening voor hyperaldosteronisme
Prevalentie primair hyperaldosteronisme 0.5 % to 2
% in ongeselecteerde hypertensieven ~ 5% na
verwijzing
Hypokaliemie in 50-80 % aanwezig (normaal kalium
in 20-50 % !)
Kans op genezing hypertensie en in geval
bijnierhyperplasie spironolacton of eplerenon (for
men) effectiever
Hyperaldosteronisme
-
natriumretentie
AGT
renine
+
ATI
+
ATII
+
aldosteron
ACE
plasma
aldosterone
plasma
renin
kaliumverlies
increased
decreased
Primary hyperaldosteronism
increased
increased
Secondary hyperaldosteronism
decreased
decreased
Pseudohyperaldosteronism
Initiële test
‘s ochtends, zittend
- kalium, natrium (evt. bicarbonaat)
- plasma aldosteron
- plasma renine
Aldosterone/Renin Ratio (ARR)
(activiteit of concentratie)
Alfa-blokkers en/of NDP/lang werkende DP calciumblokkers
Normaal kalium, stop oestrogenen, GEEN drop/zoethout
Stop kaliumsparende diuretica en beta blokkers ≥ 4 weken,
ACE/ARB>2 weken
Drop of zoethoutthee
Cholesterol
Pregnenolon
Progesteron
17a-OH-pregnenolon
11-deoxycorticosteron
Corticosteron
ALDOSTERON
17a-OH-progesteron
glycerizinezuur
-
11-deoxycortisol
CORTISOL
11- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
MR
CORTISON
Non suppressibility with NaCl load
Sens
Zout bel. test 96%
Spec
93%
NaCl capsules 3 x 2 gram 3 dagen
Aldosteron-excretie urine > 39 nmol/24 hr
Na-uitscheiding > 200 mmol/24 hr
Primair hyperaldosteronisme
Aldosteron prod. adenoom
• genezing 30-60 %, beter >90%
mutatie KCNJ5 (40%) = kalium
efflux → calcium influx → aldosteron
productie
Scholl, Nat Genet 2013; Choi M, Science
2011; Scholl, PNAS 2011
Bilaterale bijnierhyperplasie
• Spironolacton of eplerenon
(for men) effective
Vervolg casus
Lab: PRA 0.5 ngA1/ml/hr, aldosteron 0.30 nmol/l, ratio <0.7
Urine: Natrium 245 mmol/24 uur, Kalium 45 mmol/24 uur
Conclusie ?
Verder beleid ?
Behandelen?
CBO 2011
Misclassificatie
• Test karakteristieken van 2 bloeddruk metingen tijdens
2 visites voor diagnose hypertensie
• PPV~ 10-50% op diagnose hypertensie
Marshall, BMJ 2010/Med Dec Making 2006
Life-time risk
Lloyd-Jones, JAMA 2012
NICE richtlijn
• NICE guideline: behandelen als ABPM bij ≥ 150/95
mmHg en bij 135/85-150/95 mmHg ~ CVR/TOD
NICE 2011
Hoe behandelen?
Cambridge schema
Jong, West-Europees
1:
Oud, Afrikaans
A (of B)
C (of D)
A+C
2:
3:
Resistente HT
A+C
A+C
+
D
4: E = Evaluatie
E(plerenon)
5: Beta blokker / Alfa blokker
Dickerson J. & Brown M., Lancet 1999
Kaplan Meier for Primary Endpoint
Cumulative event rate
ACEI / HCTZ
20% Risk Reduction
650
CCB / ACEI
526
p = 0 .0002
Time to 1st CV morbidity/mortality (days)
HR (95% CI): 0.80 (0.72, 0.90)
INTERIM RESULTS Mar 08
Samenvatting
• Hypertensie bij jong= zoeken naar uitlokkende/
wegneembare factoren obv PDC’s (anamnese, lich.
ond., lab.), evt. PRA, aldosteron.
• Bij de behandeling rekening houden met slechte
voorspellende waarde spreekuurmeting en afwegen
korte vs lange termijn risico.
• Gezien slechte predictieve waarde spreekuurmeting ~
behandelen obv ABPM
Een wat oudere hypertensieve diabeet
65 jarige man, verwezen door cardioloog ivm hypertensie. Bekend
met coronarialijden (NYHA II/IV) en diabetes mellitus type 2.
Med. metoprolol ZOC 100 mg, HCTZ 12.5 mg, lisinopril 20 mg,
Ascal, simvastatine, metformine
Bloeddruk 170/75 mmHg liggend,154/73 mmHg staand na 1. min.
Lab.: K 4.0 mmol/l, kreat 140 umol/l , glucose 8 mmol/l, HbA1C 52
mmol/mol.
ECG: SR, doorgemaakt OWI ?, geen LVH
Urine: micralb/kreat 12.8 mg/mmol.
Differentiaal diagnose
Geisoleerde systolische hypertensie bij DM type 2 met
micro- en macrovasculaire schade
Differentiaal diagnose ?
Essentieel
+/- witte jas effect ?
Renovasculair
Autonome dysfunctie
Wat zou je doen ?
ABM, 96% geslaagde metingen, slaap: slecht
DagGem: 163/76 mmHg, NachtGem: 182/85 mmHg
Reversed Dip
Niet dippen of reverse dippen
•
Slapeloosheid, OSAS
•
Diabetes mellitus, nierinsufficientie, hartfalen
•
Ouderen of van Afrikaanse afkomst
•
Secundaire hypertensie: Cushing, Conn, NAS
•
Autonomoom falen: m. Parkinson, bij diabetes
Dipping status en CV risk
Verdecchia, Hypertension 2012
65 jarige man, verwezen door cardioloog ivm hypertensie. Bekend
met coronarialijden (NYHA II/IV) en diabetes mellitus type 2.
Med. metoprolol ZOC 100 mg, HCTZ 12.5 mg, lisinopril 20 mg,
Ascal, simvastatine, metformine
Bloeddruk 170/75 mmHg liggend,154/73 mmHg staand na 1. min.
Lab.: K 4.0 mmol/l, kreat 140 umol/l , glucose 8 mmol/l, HbA1C 52
mmol/mol.
ECG: SR, doorgemaakt OWI ?, geen LVH
Urine: micralb/kreat 25.6 mg/mmol.
ABPM:DagGem: 163/76 mmHg, NachtGem: 182/85 mmHg
Natriumbeperking
14 consecutive pnts referred with RHT
Age 49±13 jaar, 60% male, 53% white
UNa 240+/-70 mmol/24 hrs (normal 100
mmol/ 24 hrs)
12 pnts with RHT
Low salt (50 mmol/24 hrs)
∆ 20 mmHg
High salt (250 mmol/24 hrs)
∆ 10 mmHg
Pimenta, Hypertension 2009:475
MR antagonists
• Lower PRA, but not aldosterone predicts BP
response ~ volume overload
R amlodipine 10 mg ~ enkeloedeem ~ Lerdip 20 mg
R Lasix retard 60 mg icm spironolacton 25 mg
Med. metoprolol ZOC 100 mg, Lasix ret. 60 mg, lisinopril 20 mg,
spironolacton 25 mg, Lerdip 20 mg, Ascal, simvastatine
Geen bijw. of orthostase.
Spreekuur 154/70 mmHg liggend -130/65 mmHg staand
ABPM:DagGem: 138/68 mmHg, NachtGem: 125/70 mmHg
Lab. K 4.5 mmol/L, kreat 175 umol/L.
Urine: microalb./kreat 8.5 mg/mmol.
Cardiovascular events according to increasing
difference between ambulatory and office BP
Verdecchia, P. et al., Hypertension 1997
ACCORD
ROADMAP
ALTITUDE
Age
62
58
65
GFR
92
85
52
Baseline BP
139/76
136/80
135/74
Microalb/kreat
14 mg/g
4 mg/g
200 mg/g
Retinopathy
49%
?
37%
CVD%
34
30 (almost all CAD)
48
Target BP
119/64
126/74
133/73
Outcome
Geen verschil in
HVZ
Minder
microalbuminurie
Geen verschil in
HVZ
Verhoogd risico op
overlijden door HVZ
Samenvatting
• Hypertensie bij ouderen/hoog CVR
• Vaak volume afhankelijk ~ niet dippen (CD>>AB)
• Bij diabetes: vaker resistent (CAVE autonome
dysfunctie)
• Lower ≠ better: accepteer microalb. indien target
bereikt (<140/90 mmHg bij HVZ/DM en <150-160
mmHg bij 70+ zonder HVZ/DM)
Welke screening ?
• Bij laag-onderdrukt renine/PRA + meetbaar aldosteron direct
zoutbelastingstest.
2 liter NaCl 0.9% in 4 uur
Na-uitscheiding > 200 mmol/24 hr
R NaCl capsules 3x 2 gram 3 dagen
plasma aldosteron <235 pmol/L
urine aldo. >39 nmol=14 ugr/24 hr
Sens 72%
Sens 96%
Spec 91%
Spec 93%
Adrenal venous sampling
Aldosterone / cortisol
(A/C right/ A/C left)
222 / 17.1
13.0
8.49 / 18.4
0.47
3.70 / 1.05
3.50
-continuous ACTH administration
-selectivity: cortav/cortperif>3
-lateralisation: A/C ratio L-R or R-L>4
Courtesy of Jaap Deinum
AVS of CT
38 artikelen, 950 pat.
?
Terecht geopereerd (67%) *
Terecht niet geopereerd*
24.8%
37.4%
Unilaterale aldosteronproduktie = adenoom,
volgens CT-scan
19.1%
3.9%
Had geopereerd
moeten worden*
Onterecht geopereerd (33%) *
*: terecht/onterecht indien AVS juist
Kempers et al. 2009
Welke ratio ?
Aldosterone/Renin Ratio (ARR)
aldosterone
renin
ARR
ng/dl
ng/ml/hr
<20
nmol/L
nmol/L/hr
<0.71
nmol/L
mE/L
<0.091
AVS of CT ?
• Onterecht niet geopereerd: MRA
• Onterecht geopereerd ?
N=40 patienten met APA zonder lateralisatie
Sukor N, JCEM 2009
Prevalentie nierarteriestenose: een metaanalyse van 40.125 patienten
40
Bilateral
Unilateral
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
De Mast et al.
PA
D
C
H
F
A
A
A
H
T
R
ef
/S
ev
+H
T
D
M
F
ES
R
C
VA
A
G
C
er
ly
El
d
H
yp
er
t
en
s
io
n
0
Streefwaarde:Ontarget
Ramipril
Telmisartan
Combination
N
Age
% females
8576
66.4
27.2
8542
66.4
26.3
8502
66.5
26.5
% CAD
% Stroke/TIA
74.4
21.0
74.5
20.6
74.7
20.9
36.7
141.8/82.1
38.0
141.7/82.1
37.9
141.9/82.1
73.7
73.6
73.4
% Diabetes
BP
GFR
Ontarget, NEJM 2008; Lancet 2008
Ontarget: time to first CVE
Bloeddruk
Ramipril
Telmisartan
Combination
136/78
135/77
134/76
Ontarget, NEJM 2008; Lancet 2008
MRA bij diabeten met RHT
• N=119 pnten met DM2 en >130/80 mmHg bij ABPM
• Spironolacton 25 mg → 50 mg als BP≠130/80 mmHg.
• ABPM voor en na (16 weken)
• Hyperkaliemie: discontinuatie in 1, dosisreductie in 3
Oxlund, ESH 2013
ACCORD
ROADMAP
ALTITUDE
Age
62
58
65
GFR
92
85
52
Baseline BP
139/76
136/80
135/74
Microalb/kreat
14 mg/g
4 mg/g
200 mg/g
Retinopathy
49%
?
37%
CVD%
34
30 (almost all CAD)
48
Target BP
119/64
126/74
133/73
Outcome
No difference in
CV events
Reduction in
microalbuminuria
Tendency to
increased CVE
(p=0.12 for PE)
Decreased risk of
non-fatal stroke
No differences in
composite endpoint
Increased risk of
death from CVE
Stopped
prematurely for
futility
Diastolic BP and risk of MI/Stroke
Messerli, Ann Intern Med 2006: 884
HYVET Trial: Outcomes
Blood pressure in the Intention-to-Treat Population
180
Target BP <150/80 mmHg
170
Blood Pressure (mmHg)
160
150
140
Placebo
130
120
Indapamide SR +/perindopril
I
110
100
90
80
70
0
1
2
3
4
5
Follow-up (years)
Copyleft Clinical Trial Results. You Must Redistribute Slides
N Engl J Med 2008;358/ACC 2008
HYVET Trial: Outcomes
Main Fatal and Nonfatal End Points in the Intention-to-Treat Population
Fatal stroke
NNT 60
All cause mortality
NNT 20
N Engl J Med 2008;358/ACC 2008
HYVET Trial: Outcomes
Blood pressure in the Intention-to-Treat Population
180
Target BP 150/80 mmHg
170
Blood Pressure (mmHg)
160
150
140
Placebo
130
120
Indapamide SR +/perindopril
I
110
100
90
80
70
0
1
2
3
4
5
Follow-up (years)
Copyleft Clinical Trial Results. You Must Redistribute Slides
N Engl J Med 2008;358/ACC 2008
Beslisboom PRA en aldosteron
plasma renine
onderdrukt/laag
hoog
plasma aldosteron
laag
-high-renin hypertension
-nierarteriestenose
-maligne hypertensie
-reninoom
- drop/zoethoutthee
- hypercortisolisme
- teveel deoxycortison
- Liddle syndroom
- AME
- Gordon’s syndrome
hoog
- low renin hypertension
- APA/ bijnierhyperplasie
- GRA
HYVET Trial: Outcomes
Main Fatal and Nonfatal End Points in the Intention-to-Treat Population
Fatal stroke
NNT 60
All cause mortality
NNT 20
N Engl J Med 2008;358/ACC 2008
Diastolic BP and risk of MI/Stroke
Messerli, Ann Intern Med 2006: 884
Cambridge schema
Jong, West-Europees
1:
Oud, Afrikaans
A (of B)
C (of D)
A+C
2:
3:
Resistente HT
A+C
A+C
+
D
4: E = Evaluatie
Add: E(plerenone)
5: Beta blokker / Alfa blokker
Laragh et al. Textbook Hypertension Volume 1.
Cambridge schema
Jong, West-Europees
1:
A (of B)
Oud, Afrikaans
C (of D)
Dickerson J. & Brown M., Lancet 1999
Oslo studie
• RCT in 785 mannen 40-49 jaar met bloeddruk
150-179 mmHg, behandeld voor 5 jaar
Bloeddruk >160/100 mmHg: ARR ∆7-8% ~
NNT = 13 in 5 jaar
Helgeland, Am J Med 1980
‘Essentieel’ vs Secundair
Trinquart L, Hypertension 2010
Outcome of APA following surgery:
Age < 44 jr OR 6.2 for cure vs Age ≥ 44 jr
Celen O, Arch Surgery 1996
Ontarget: Baseline Characteristics
Ramipril
Telmisartan
Combination
N
Age
% females
8576
66.4
27.2
8542
66.4
26.3
8502
66.5
26.5
% CAD
% Stroke/TIA
74.4
21.0
74.5
20.6
74.7
20.9
36.7
141.8/82.1
38.0
141.7/82.1
37.9
141.9/82.1
73.7
73.6
73.4
% Diabetes
BP
GFR
Ontarget, NEJM 2008; Lancet 2008
Ontarget: time to first CVE
Bloeddruk
Ramipril
Telmisartan
Combination
136/78
135/77
134/76
Ontarget, NEJM 2008; Lancet 2008
ACCORD
ROADMAP
ALTITUDE
Age
62
58
65
GFR
92
85
52
Baseline BP
139/76
136/80
135/74
Microalb/kreat
14 mg/g
4 mg/g
200 mg/g
Retinopathy
49%
?
37%
CVD%
34
30 (almost all CAD)
48
Target BP
119/64
126/74
133/73
Outcome
No difference in
CV events
Reduction in
microalbuminuria
Tendency to
increased CVE
(p=0.12 for PE)
Decreased risk of
non-fatal stroke
No differences in
composite endpoint
Increased risk of
death from CVE
Stopped
prematurely for
futility
Systolic Blood Pressure Over
Time
ACEI / HCTZ
N=5733
CCB / ACEI
mm Hg
N=5713
130mmHg
Difference of 0.7 mmHg p<0.05*
129.3 mmHg
Month
Patients
5731
5709
5387
5377
5206
5154
4999
4980
*Mean values are taken at 30 months F/U visit
DBP: 71.1
DBP: 72.8
4804
4831
4285
4286
2520
2594
1045
1075
Hypertensie en CVR
8x
8
7
6
CV sterfte
5
4x
4
3
2
2x
1
0
120/80
140/90
160/100
SBP/DBP (mm Hg)
Chobanian AV et al. JAMA. 2003;289:2560-2572.
Lewington S et al. Lancet. 2002;360:1903-1913.
180/110
Kaplan Meier for Primary
Endpoint
Cumulative event rate
ACEI / HCTZ
20% Risk Reduction
650
CCB / ACEI
526
p = 0 .0002
Time to 1st CV morbidity/mortality (days)
HR (95% CI): 0.80 (0.72, 0.90)
INTERIM RESULTS Mar 08
Protocol to avoid contrast nephropathy
• eGFR<45 ml/min of eGFR<60 ml/min + diabetes
of 2 of meer RF (leeftijd>70 jr, CHF,
atherosclerosis)
• Day of contrast no diuretics, NSAID’s and other
nephrotoxic medication
• Sodiumbicarbonate iv (1,4%) 1 uur (3 ml/kg/hr)
before, continue 1 ml/kg/hr during and up to 6 hr
after contrast
• Serumkreatinine 24 hr post contrast
Monogenetische varianten
• HT jonge leeftijd met positieve familie anamnese
• 6 vormen, waarvan 5 invloed op NaCl transport in de nier
• Afwijkend PRA (laag/onderdrukt), aldosteron (laag, behalve
in GRA)
Witte Jas hypertensie en witte jas effect
Witte jas effect
Witte jas hypertensie
Nurse: r = 0.60; Self (home): r = 0.75
BMJ 2002;325:254
Prevalentie WCH: data > 5000 pnten
Dolan E, BP Monit. 2004
Witte jas hypertensie
• Thuis bloeddrukmeten (compliantie !)
• Ambulante bloeddrukmeting (gouden standaard)
Compliantie
Patients remaining on
therapy at 1 year (%)
100
80
64
58
60
50
43
40
38
20
0
Ang II
receptor
antagonists
ACE
inhibitors
Bloom BS. Clin Ther 1998; 20 671-681
Calcium
channel
blockers
ß-blockers
Diuretic
Hoe weet je of iemand compliant is ?
•
Vriendelijk naar informeren
•
Pillen laten meenemen en tellen
•
Apotheek bellen
•
Pols ~ beta blockers, kalium ~ diuretica (thiazides en
kaliumsparend), uraat ~ lis diuretica, PRA ~ renine
blokkers, ACE ~ ACE remmers
•
Stop alle medicatie, evalueer effect en begin
opnieuw
•
Meet serumspiegels van anti-hypertensiva
Ongunstige life-style
•
Overgewicht: per 10 kg gewicht ∆ 6 /4 mmHg
•
Te veel alcohol (> 4 IE/dd)
2 liter
10 liter
Overmatig zoutgebruik
•
In populaties met weinig zoutgebruik (<50 gr/24 uur)
komt HT niet voor
•
Het gemiddelde NL dieet bevat 150-200 mmol zout
•
Vermindering van de hoeveelheid zout met 75 mmol/
24 uur geeft een gemiddelde RR verlaging van 5/3
mmHg, maar kent grote individuele verschillen
•
Werking ACE-remmers/ARB en diuretica enorm
afhankelijk van hoeveelheid zoutinname.
Middelen die de bloeddruk verhogen
Raise
Blood
Pressure
Interfere
With
Therapy
Anabole steroiden
Yes
No
Patient
Caffeine
Yes
No
Patient
Cocaine
Yes
Yes
Patient
Ethanol
Yes
No
Patient
Nicotine
Yes
No
Patient
Orale anticonceptiva
Yes
Yes
Patient
Sympathomimetica
Yes
No
Patient or clinician
Yes
Patient or clinician
Substance
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents Yes
Source of
Substance
Middelen die de bloeddruk verhogen
Raise
Blood
Pressure
Interfere
With
Therapy
Source of
Substance
Chlorpromazine
Yes
No
Clinician
Corticosteroiden
Yes
Yes
Clinician
Cyclosporine
Yes
No
Clinician
Erythropoietine
Yes
No
Clinician
Tricyclische antidepressiva
Yes
No
Clinician
Substance
Secondary hypertension after referral
Sinclair
Anderson
Omura
1987
1994
2003
Aantal pat
3783
4429
1020
Prim HT (%)
92
90
91
Renale HT (%)
5.6
1.8
excl
Renovasc HT (%)
0.7
3.3
0.5
Prim hyperaldo (%)
0.3
1.4
6.0
S. van Cushing (%)
0.1
0.6
2.0
Feochromocytoom (%)
0.1
0.3
0.6
Obstructive sleep apnoea ?
Initial screening test for PA
Considerations:
No spironolactone, no beta blockers (stop >6 weeks)
ACE, ARB and HCT: ↑ PRA, +/- aldosterone (stop >2
weeks)
CCB and alfa-blockers: no influence
Try to get normal potassium concentrations !
3. HT under 30 with no apparent cause
No apparent cause: no adiposity, DM, renal disease
Work-up as in “every hypertensive patient” and “therapy
resistant hypertension”
+ family history HT: ARR (+ FMD)
- family history HT: ARR + FMD
How to check adherence ?
•
Ask about compliance (in a nice way)
•
Pill count
•
Contact local pharmacy
•
Stop all medication and evaluate effect
•
Pulse rate ~ beta blockers, potassium ~ thiazides
and urate ~ loop diuretics
•
Measure serum levels of anti-hypertensive drugs
Primary hyperaldosteronism ?
Causes:
prev (%)
– aldosterone producing adenoma
64
– idiopathic hyperaldosteronism
32
– apparent mineralocorticoid excess
<2
– glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism
<2
– aldosterone-prod adrenocortical carcinoma 1
– assoc. with other endocrine diseases
<1
Causes of refractory hypertension
• Poor compliance and adherence to therapy
• White coat hypertension/effect
• Continued intake of drugs that raise blood pressure
• Unsuspected secondary cause
Effect of revascularization on blood
pressure
• may improve blood pressure control and therefore CV risk
Van Jaarsveld, NEJM 2000
Who should be screened for PA ?
Prevalence of primary aldosteronism 0.5 % to 2 % in
unselected hypertensive patients (rare)
Hypokalemia present in 50-80 % (normal potassium
in 20-50 % !)