Infectie en afweer
TT bundels oefenen
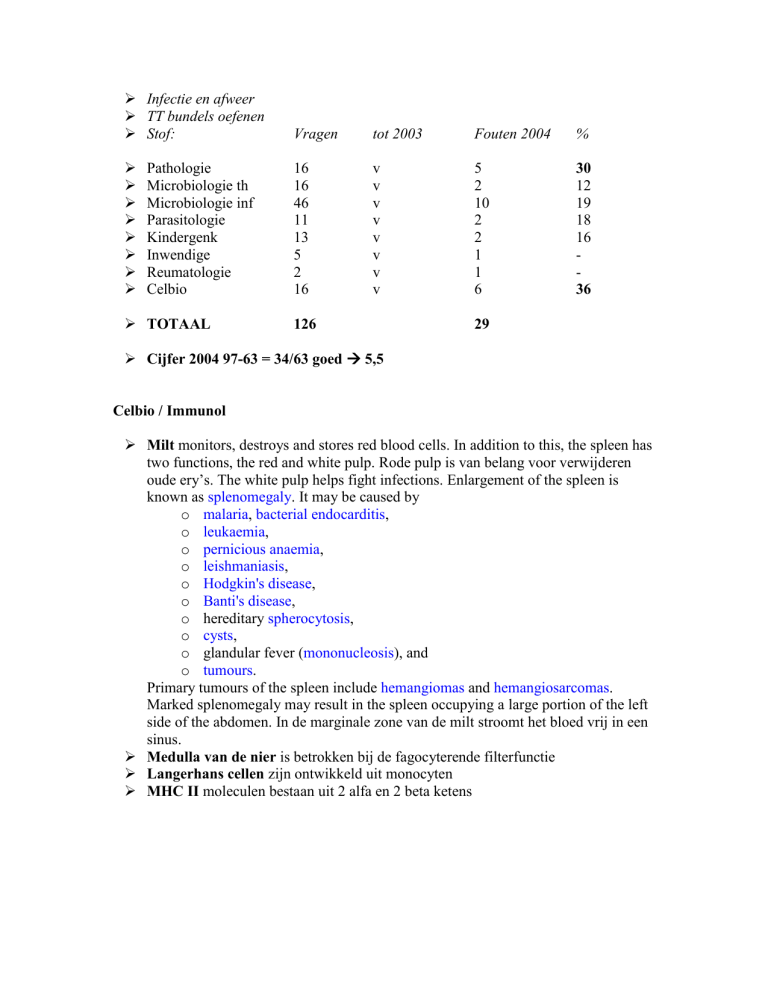
Stof:
Vragen
tot 2003
Fouten 2004
%
16
16
46
11
13
5
2
16
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
5
2
10
2
2
1
1
6
30
12
19
18
16
36
Pathologie
Microbiologie th
Microbiologie inf
Parasitologie
Kindergenk
Inwendige
Reumatologie
Celbio
TOTAAL
126
29
Cijfer 2004 97-63 = 34/63 goed 5,5
Celbio / Immunol
Milt monitors, destroys and stores red blood cells. In addition to this, the spleen has
two functions, the red and white pulp. Rode pulp is van belang voor verwijderen
oude ery’s. The white pulp helps fight infections. Enlargement of the spleen is
known as splenomegaly. It may be caused by
o malaria, bacterial endocarditis,
o leukaemia,
o pernicious anaemia,
o leishmaniasis,
o Hodgkin's disease,
o Banti's disease,
o hereditary spherocytosis,
o cysts,
o glandular fever (mononucleosis), and
o tumours.
Primary tumours of the spleen include hemangiomas and hemangiosarcomas.
Marked splenomegaly may result in the spleen occupying a large portion of the left
side of the abdomen. In de marginale zone van de milt stroomt het bloed vrij in een
sinus.
Medulla van de nier is betrokken bij de fagocyterende filterfunctie
Langerhans cellen zijn ontwikkeld uit monocyten
MHC II moleculen bestaan uit 2 alfa en 2 beta ketens
Figure 1 MHC II: 2 alfa en 2 beta ketens
Immunoglobuline Bij de mens worden 5 Ig klassen onderscheiden. Fc gedeelte op
de zware keten bepaalt de effectorfuncties van een Ig molecuul. In 1 Ig molecuul
zijn de twee zware ketens hetzelfde. De diversiteit in Ig wordt oa bereikt door gen
herschikking in voorloper B lymfo’s in het beenmerg.
IgM: primaire immuunrespons. is het grootse molecuul en te vinden in serum,
waar het zorgt voor de klontering bij verkeerde transfusie
IgA: 15-20% van het Ig in bloed, maar meer langs tractus dig.
IgG secundaire immuunrespons. is a monomeric immunoglobulin, built of two
heavy chains γ and two light chains. Each molecule has two antigen binding sites.
This is the most abundant immunoglobulin and is approximately equally
distributed in blood and in tissue liquids. This is the only isotype that can pass
through the placenta, thereby providing protection to the fetus in its first weeks of
life before its own immune system has developed. It can bind to many kinds of
pathogens, for example viruses, bacteria, and fungi, and protects the body against
them by complement activation (classic pathway), opsonization for phagocytosis
and neutralisation of their toxins. There are 4 subclasses: IgG1 (66%), IgG2 (23%),
IgG3 (7%) and IgG4 (4%).
o IgG1, IgG3 and IgG4 cross the placenta easily.
o IgG3 is the most effective complement activator, followed by IgG1 and
then IgG2. IgG4 does not activate complement.
o IgG1 and IgG3 bind with high affinity to Fc receptors on phagocytic cells.
IgG4 has intermediate affinity and IgG2 affinity is extremely low.
IFN (interferon) gamma Onder invloed vertonen macrofagen een verhoogde
fagocytose
HLA (MHC) is the human version of the major histocompatibility complex
(MHC), a gene family that occurs in many species. Genes in this complex are
separated into three basic groups: class I, class II, and class III. In humans, the
HLA-B gene and two related genes, HLA-A and HLA-C, are the major genes in
MHC class I. De kans dat broer en zus HLA identiek zijn is kleiner dan 50% (alleen
100% bij tweelingen). Het verminderd tot expressie brengen van HLA moleculen
op het oppervlak van een tumor is een mechanisme om aan het immuunsysteem te
ontsnappen. Dendritische cellen zijn HLA-A cellen. Via HLA I gerestricteerde
cytotoxiciteit kunnen CD8 positieve T cellen viraal geinfecteerde cellen doden. Het
polymorfisme van het HLA manifesteert zich binnen de populatie maar niet binnen
het individu. Bij transfusie van alleen lichaamscellen letten op HLA. (Ery’s hebben
geen HLA). MHC moleculen blijven het gehele leven hetzelfde
BALT (bronchus associated lymphoid tissue) komen IgA producerende B cellen voor.
FDC De binding van immuuncomplexen aan FDC (Follicular Dendritic Cells) in
follikels speelt waarschijnlijk een belangrijke rol bij de ontwikkeling van geheugen
B-cellen. FDC in de follikels zijn in staat immuuncomplexen te binden
T cellen Bij de kiemcentrumreactie in een lymfeklier spelen CD4T een belangrijke
rol. Functionele T lymfo’s kunnen peptiden, gebonden aan HLA herkennen. bindt
vooral aan (primaire) peptiden, B cel vooral aan hele intacte eiwitten. Worden in de
thymusschors geselecteerd op matige herkenning van MHC. CD4 T Helper cellen
produceren na activatie cytokines, CD8 positieve T lymfo’s kunnen antigene
peptiden in de groeve van MHC I moleculen aan het opp van een lichaamscel
herkennen
B cel Bij de isotype switching van een differentierende B-cel blijft de
antigeenspecificiteit van het antilichaam behouden. B-lymfo’s kunnen na activatie
door antigeen differentieren in plasmacellen dan wel geheugencellen De isotype
switch van B cellen is T cel afhankelijk. Bindt aan gehele eiwitten. In de B cel
follikels van lymfoide organen vindt geheugenvorming plaats
Storingen immuunststeem en gevolgen
o Complementsysteem: bacteriele infecties
o B cel systeem: bacteriele, polio, pneumocystis
o T cel systeem: virale infecties door uitval CD8 cellen
o Fagocyten: Leishmania, Pneumocystis, TBC, Lepra
Lymfklier Secundaire lymforganen zijn nodig voor de inductie van een effectieve
antigeenspecifieke immuunrespons en immunologische geheugenvorming. In de
paracortex zijn cellen aanwezig met MHCII op het oppervlak. Lymfocyten verlaten
de lymfeklier via het bloed
MAC (Membrane Attack Cascade) is the cytolytic endproduct of the complement
cascade; it forms a transmembrane channel, which causes osmotic lysis of the target
cell. Kupffer cells are specialized macrophages located in the liver
Complement Niet ieder complementfragment is in staat bacterien en virussen te
lyseren. Complement C3b die zo belangrijk is voor fagocytose wordt zowel via
klassieke als alternatieve route geproduceerd. The three (Classic, Alternative,
Lectine) complement pathways all generate homologous variants of the protease
C3-convertase. C3-convertase cleaves and activates component C3, creating C3a
and C3b and causing a cascade of further cleavage and activation events.
o C3b binds to the surface of pathogens leading to greater internalization
by phagocytic cells.
o C5a is an important chemokine, helping recruit inflammatory cells.
o C5b initiates the membrane attack pathway, which results in the:
o MAC membrane attack complex (MAC), consisting of C5b, C6, C7, C8,
and polymeric C9. MAC is the cytolytic endproduct of the complement
cascade; it forms a transmembrane channel, which causes osmotic lysis of
the target cell.
o Kupffer cells help clear complement-coated pathogens.
Paracrien cytokinen werken alleen op de naburige ecellen
Integrin, or integrin receptor, is an integral membrane protein in the plasma
membrane of cells. It plays a role in the attachment of a cell to the extracellular
matrix (ECM) (especially in growth cone axon guidance) and in signal transduction
from the ECM to the cell.
oxidatieve killing door fagocyten berust in belangrijke mate op de synthese van
zuurstofradicalen
EIA: Enzyme Immuno Assay The Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay
(ELISA for short) is a biochemical technique used mainly in immunology to detect
the presence of an antibody or an antigen in a sample.
Parasitologie
Entamoeba histolytica Bij asymptomatische infectie kan in de ontlasting het
cystestadium gevonden worden. In de faeces van een patient met een enige tijd
bestaande acute darmamoebiasis kunnen trofozoieten (amoebenvormen) van
Entamoeba histolytica worden aangetroffen. Infecties met Entamoeba dispar komen
veel vaker voor dan die met E. histolytica
Darmprotozoen: infectie via de mond. Niet via trofozoieten, maar cysten?
Giardia Lamblia asymptomatische infectie hoeft niet behandeld te worden. Bij
veel individuen zal infestatie geen klinische gevolgen hebben, men spreekt dan van
asymptomatisch dragerschap. Wanneer men symptomen vertoont die worden
veroorzaakt door een infectie met G. duodenalis, spreekt men van giardiasis. Deze
symptomen zijn over het algemeen karakteristieke malabsorptie problemen zoals:
diarree, gepaard gaande met buikklachten, misselijkheid, algehele malaise,
gasvorming en vettige stinkende ontlasting. Vaak is hiervan gewichtverlies,
zwakheid en chronische vermoeidheid het gevolg. diagnose niet uit kweek, alleen
uit serologie. Giardia infection is a concern for people camping in the wilderness or
swimming in contaminated streams or lakes, especially the artificial lakes formed
by beaver dams (hence the popular name for giardiasis, "Beaver Fever").
Echinococcosis (Giardiasis) is in NL niet langer endemisch. Infection with
Echinococcus results in hydatid disease, also known as echinococcosis. This is a
potentially fatal parasitic disease. via uitwerpselen honden. Infection with E.
multilocularis results in the formation of dense parasitic tumors in the liver,
lungs, brain, and other organs. This condition, also called alveolar hydatid
disease is likely to be fatal.
Figuur 1 Giardia lamblia
Varkenslintworm Taenia solium is een lintworm die als gastheren de mens en
varkens heeft. De mens kan echter zowel lintwormdrager als cysticercusdrager (zie
verderop) zijn. Lintwormen komen wereldwijd voor maar zijn zeldzaam in westerse
landen (hygiëne) en T. solium ook in moslimlanden (waar men geen varkens eet).
De lintworm kan zeer lang worden (ca 5 meter) en bestaat uit een kop of scolex die
zich in het slijmvlies van het maagdarmkanaal heeft verankerd. Voedsel wordt door
de worm via de huid uit het maagdarmkanaal opgenomen. Een mens met een
lintworm merkt daar meestal weinig van. Wat vage buikklachten. Het is zeker niet
zo dat zo iemand altijd sterk vermagert. Wel kunnen meestal de lintwormsegmenten
in de ontlasting worden gevonden als de worm eenmaal voorplantingsrijp is.
Behandeling is tamelijk eenvoudig met een korte kuur van een lintwormdodend
middel zoals bijvoorbeel praziquantel. De eieren van de varkenslintworm zijn
infectieus voor de mens. Is de mens ook de tweede tussengastheer, dan kunnen er in
velerlei organen lintwormkysten ontstaan, die vooral doordat ze ruimte innemen
klachten kunnen geven. De hersenen zijn hiervoor het gevoeligst (met als
symptomen uitvalsverschijnselen, of epilepsie) maar ook in de longen en in de lever
kunnen lintwormkysten ontstaan. Bij het barsten van een lintwormkysten kan wel
eens een hevige allergische reactie optreden door het plots in het lichaam vrijkomen
van veel lichaamsvreemd lintwormmateriaal; operaties op dergelijke kysten moeten
om deze reden behoedzaam worden verricht. secundair ziektebeeld cysticerosis
(blaaswormziekte). Geeft veel schade aan gastheer relatie met mens als gastheer
jong in de evolutie
Varkenslintworm Cysticercosis, or neurocysticercosis, is the most common
parasitic infection of the central nervous system worldwide. It is caused by
BLAASWORMEN of the tapeworm (VarkensLINTWORM; A. van
Leeuwenhoek), Taenia solium, normally found in pork. The larvae, called cysticerci
(singular cysticercus; also called bladder worms) form cysts in the body. De
laboratoriumdiagnostiek van cysticerosis is in de eerste plaats gebaseerd op het
aantonen van specifieke antistoffen in het serum van de patient.
Varkenslintworm Teniasis If these VARKENSLINTworms are found in the
intestine, they cause a different disease that is called teniasis. Cysticercosis occurs
when Taenia solium eggs enter the stomach. This can be from food or water
contaminated with infected human fecal material.
Spoelworm (Ascaris lumbricoides) is een darmparasiet die vroeger veel voorkwam
maar tegenwoordig nog maar zelden in Nederland wordt waargenomen. Wereldwijd
is echter misschien wel een kwart van de wereldbevolking besmet. De aandoening
van het besmet zijn met ascaris lumbricodes heet ascariasis.De spoelworm is een
rondworm van enige mm dik en tot ca 15-20 cm lang (vrouwtjes; de mannetjes
blijven wat kleiner).
Zweepworm (Trichuris trichiura) is een lichtgele tot witte parasiet van 3 tot 5 cm;
een van de grotere van NL. Besmetting gebeurt via huisdieren die de eieren in hun
ontlasting achterlaten. De mens neemt deze tot zich via aarde of grond.
Aarsmade: Enterobius vermicularis. 1 cm. grote rolronde wormpjes in ontlasting.
Kleinste rondwormsoort van NL. Eieren al kort na het leggen infectieus voor de
mens. Geen resten van gastheerwisseling uit eerder evolutie stadium; waarschijnlijk
wisselt hij nog steeds van gastheer
Endemische wormen in NL
o Taena saginata (Runderlintworm)
o Enterobius vermacularis (Aarsmade)
o Ascaris lumbricoides (Spoelworm)
o Giardia lamblia
o Toxoplasma gondii
o Cryptosporidium spp.
Visceral Larva Migrans veroorzaakt door infectie via honden en katten faeces
Figure 2visceral larva migrans
Malaria Ondanks profylaxen is volledige resistentie tegen malaria niet mogelijk.
Malaria Stadium bij overdracht mug op mens: sporozoietstadium
Malaria, Merozoieten: Directe ontw stadium van P. falciforme en malariae, maar
niet van vivax en ovale, die ontwikkelen in hypnozieten die kunnen overwinteren in
de mens
Malaria, Hypnozoieten: Some P. vivax and P. ovale sporozoites do not
immediately develop into exoerythrocytic-phase merozoites, but instead produce
hypnozoites that remain dormant for periods ranging from several months (6–12
months is typical) to as long as three years. After a period of dormancy, they
reactivate and produce merozoites. Hypnozoites are responsible for long incubation
and late relapses in these two species of malaria. Approximately 50% of P. vivax
malaria cases in temperate areas involve overwintering by hypnozoites (i.e.,
relapses begin the year after the mosquito bite).
Malaria, vivaxmalaria: koortsaanvallen om de 48 uur (m. tertiana)
Malaria, P. malariae: koortsaanvallen om de 72 uur (m. quartana)
Schistosomen:Zuigwormen. Infectie door larven (cercariae) die zich ontwikkelden
in slakken
Schistosomiasis (Acute vesicale) veroorzaakt hematurie (menstruerende jongetjes
in Afrika)
Strongyloides stercoralis transplantatie patienten die een tropenverblijf in hun
anamnese hebben kunnen een subklinische infectie ontwikkelen; By its cycle, S.
stercoralis can cause both respiratory and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Leishmania: fagocytenparasiet, geeft zichtbare kinetoplast in de fagocyt,
overdracht door sandfly. kan optreden na een half jaar geelden bij de Midd Zee te
zijn geweest. Diagnose op basis van beenmergpreparaat.
Trichomonas vaginalis: can occur in females (males rarely exhibit any symptoms
of a T. vaginalis infection) if the normal acidity of the vagina is shifted from a
healthy, semi-acidic pH (3.8 - 4.2) to a much more basic one (5 - 6) that is
conducive to T. vaginalis growth. Some of the symptoms of T. vaginalis include:
preterm delivery, low birth weight, and increased mortality as well as
predisposing to HIV infection, AIDS, and cervical cancer. T. vaginalis has also
been reported in the urinary tract, fallopian tubes, and pelvis and can cause
pneumonia, bronchitis, and oral lesions. Other symptoms include inflammation with
increasing number of organisms, greenish-yellow frothy vaginal secretions and
itching. Trichomonads reproduce by a special form of longitudinal fission, leading
to large numbers of trophozoites in a relatively short time. Cysts never form, so
transmission from one host to another is always based on direct contact between the
sites they occupy. T. vaginalis can be detected by studying discharge or with a pap
smear and culturing. With a PAP smear, infected individuals would have a
transparent "halo" around their superficial cell nucleus. Condoms are effective
at preventing infection. Metronidazole or tinidazole can treat an infection in
progress, and should be prescribed to sexual partners as well. Trichomonas
vaginalis Overdracht vindt plaats door het trofozoietstadium
Figure 3 trichomonas vaginalis
Toxoplasma is a species of parasitic protozoa whose definitive host is cats but
which can be carried by the vast majority of warm-blooded animals, including
humans. Toxoplasmosis, the disease it causes, is usually minor and self-limiting but
can have serious or even fatal effects on a fetus whose mother first contracts the
disease during pregnancy.
Pathologie
Idiotype. Unieke vorm van een antilichaam. The unique set of antigenic
determinants of the variable portion of an antibody is called "idiotope". In some
cases it can be the actual antigen-binding site, and in some cases it may comprise
variable region sequences outside of the antigen-binding site on the antibody itself.
Thus each antibody would have multiple idiotopes; and the sum of these
individual idiotopes is called as the idiotype of the antibody.
Fc receptor increase the affinity phagocytic cells have on microbes. It is a receptor
on hematopoietic cells such as macrophages, neutrophils and mast cells. They will
bind to the constant end of immunoglobulin after these antibodies have binded to
antigens. The Phagocytes cause phagocytosis and subsequent killing of the
pathogen. (de Fc receptor bevindt zich dus niet op Ig, maar juist op de fagocyt)
Astma is een type I allergie, want er is een duidelijk herkende externe oorzaak.
Eerste reactie: The bronchi (large airways) contract into spasm (an "asthma attack").
Inflammation soon follows, leading to a further narrowing of the airways and
excessive mucus production, which leads to coughing and other breathing
difficulties.
HIV Non Hodgkin bij HIV diagnose = AIDS
Hypersensitiviteit
o Type I hypersensitivity in which a person's body is hypersensitised and
develops IgE type antibodies to typical proteins. Bv Pollen
o In type 2 hypersensitivity, the antibodies produced by the immune
response bind to antigens on the patient's own cell surfaces. IgG en IgM
(Goodpasture). Bv Hemolyse
o In type 3 hypersensitivity, soluble immune complexes (aggregations of
antigens and IgG and IgM antibodies) form in the blood and are deposited
in various tissues (typically the skin, kidney and joints) where they may
trigger an immune response according to the classical pathway of
complement activation (see above). The reaction takes hours to days to
develop. Celspecifieke schade; IgG en IgM neerslag activeert complement
cascade (bij SLE)
o Type 4 hypersensitivity is often called delayed type as the reaction takes
two to three days to develop. Unlike the other types, it is not antibody
mediated but rather is a type of cell-mediated response. CD8 cytotoxic T
cells and CD4 helper T cells recognise antigen. Aspecifieke schade. Bij
een type 4 allergie is de macrofaag een van de hoofdeffectorcellen. (bv
Reuma?)
Anaphylaxis is a severe and rapid multi-system allergic reaction. Anaphylaxis
occurs when a person is exposed to a trigger substance, called an allergen, to which
they have become sensitized. Minute amounts of allergens may cause a lifethreatening anaphylactic reaction. Anaphylaxis may occur after ingestion,
inhalation, skin contact or injection of an allergen. The most severe type of
anaphylaxis—anaphylactic shock—will usually lead to death in minutes if left
untreated. door IgE Type I
SLE Meest aangedane orgaan is de huid. Verschillende antilichamen worden
gevonden.
XLA (X-linked agammaglobulinemia). The primary immune deficiency (PID)
disorder is an X-linked, recessive genetic disease characterized by a deficiency in
serum gamma globulin and a paucity of mature B cells and plasma cells. XLA is
caused by a mutation in Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), a non-receptor kinase that
plays a critical role in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling leading to the maturation
of B cells into plasma cells. As this maturation process is a key component to an
effective humoral immune response, mutations in Btk are thus manifested in
recurrent infections, particularly with encapsulated bacteria (KNO gebied en de
longen). XLA only manifests in male offspring, while females may be healthy
carriers. Common treatment for the disorder is intravenous or subcutaneous
immunoglobulin therapy.
DiGeorge syndroom is a rare congenital (i.e. present at birth) disease whose
symptoms vary greatly between individuals but commonly include a history of
recurrent infection, heart defects, and characteristic facial features. DiGeorge
syndrome is caused by a large deletion from chromosome 22, produced by an error
in recombination at meiosis (the process that creates germ cells and ensures genetic
variation in the offspring). Although researchers now know that the DGS gene is
required for the normal development of the thymus and related glands,
counteracting the loss of DGS is difficult. Some effects, for example the cardiac
problems and some of the speech impairments, can be treated either surgically or
therapeutically, but the loss of immune system T-cells (produced by the thymus) is
more challenging and requires further research on recombination and immune
function. Hierbij is het geven van transfusie risicovol
Figure 4 DiGeorge: gezichtstrekken
Levertransplantatie afstoting niet het grootste gevaar. Liver transplantation is
unique in that the risk of chronic rejection also decreases over time. Certain
patients, on the long run, manage to be weaned off all immunosupressive
medication. The exact reason for this is still unclear.
Diabetes M2 is geen auto-imm ziekte, DM1 is dat wel: een orgaanspecifieke
immuunziekte
Immunologically privileged site is any of those locations in the body--the brain,
anterior chamber of the eye, testis, renal tubule, uterus, and possibly joints and
adrenal glands--where immune response to antigens are not destructive to tissue or
is suppressed. It is necessary due to unique self-proteins that reside only in
particular tissues and do not travel through the lymphatic system. Examples of
tissue-specific proteins include myelin of the central nervous system. Such proteins
are sequestered in organs and extracellular fluid does not travel the lymphatic
system, meaning they do not come into contact with T cells during negative
selection in the thymus. Allografts to these sites are not rejected. (Cornea
transplant)
Sequestering is a procedure of isolating different types of physical processes or
different particle species by separating them geometrically in additional
dimensions of space
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease. . In MG, the autoantibodies are
directed most commonly against the acetylcholine receptor (nicotinic type), the
receptor in the motor end plate for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine that
stimulates muscular contraction.While in various similar diseases the disease has
been linked to a cross-reaction with an infective agent, there is no known causative
pathogen that could account for myasthenia. There is a slight genetic predisposition:
particular HLA types seem to predispose for MG (B8 and DR3 with DR1 more
specific for ocular myasthenia). Up to 25% have a concurrent thymoma, a tumor
(either benign or malignant) of the thymus, and other abnormalities are frequently
found. The disease process generally remains stationary after thymectomy (removal
of the thymus)
Figure 5 myasthenia gravis
Pemphigus vulgaris occurs when antibodies attack Desmoglein 3, a protein that
keeps cells bound together. Thus, cells simply fall apart, causing skin to slough
off. Although pemphigus vulgaris may occur at any age, it is quite rare in children,
and most common in the middle aged and elderly. Sores often originate in the
mouth, making eating difficult and uncomfortable. Pemphigus vulgaris often affects
people between the ages of 40-60, and mainly of Jewish or Mediterranean descent.
Some patients are associated with myasthenia gravis, but it's unusual.
Langerhans' cells are immature dendritic cells containing large granules called
Birbeck granules. On infection of an area of skin, the local Langerhans' cells will
take up and process microbial antigens before travelling to the T-cell areas in the
cortex of the draining lymph node and maturing to become fully-functional
antigen-presenting cells.
Afstoting oa. Veroorzaakt door ABO incompatibiliteit
Monoclonale antilichamen gebruikt tegen maligniteiten
Tolerantie-inductie Op de afdeling Nierziekten wordt gezocht naar manieren om
het immuunsysteem van de ontvanger zo ver te krijgen dat het eilandjes van
donoren vriendelijk ontvangt. Immunoloog dr. Cees van Kooten: “Dat noem je
tolerantie-inductie. En het komt natuurlijk bij alle soorten transplantaties van pas.
Het belangrijkste celtype bij tolerantie-inductie is de dendritische cel. Zulke cellen
zijn voorzien van lange uitsteeksels – dendrieten, vandaar de naam – en ze liggen
overal in het lichaam te wachten tot ze iets vreemds tegenkomen. Het is een soort
alarmsysteem. De laatste jaren wordt echter duidelijk dat ze ook in hun rustfase heel
belangrijk zijn: ze zijn de sleutel tot het opwekken van tolerantie.” De komende
jaren gaan onderzoekers van Nierziekten proberen dendritische cellen te kweken die
niet meer in staat zijn alarm te slaan, maar nog wel een sussende rol kunnen spelen.
Van Kooten: “Ook zullen we kijken hoe we de reactie van de dendritische cellen
kunnen sturen met toegevoegde stoffen. Dat kan bijvoorbeeld met hormonen, zoals
corticosteroïden en vitamine D3, of met een antistof die zich aan dendritische
cellen hecht op een plaats die hij nodig heeft om agressief te worden, de CD40receptor. Als je dat kort doet, tijdens het aanbieden van cellen die er hetzelfde
uitzien als het transplantaat, heb je kans dat die voortaan niet meer als indringers
worden gezien.”
Acuut reuma: T cellen begin an immune attack against, in this case, the synovium,
because some molecule in the synovium "looks like" a molecule on the offending
organism (Mycoplasma) that created the initial immune reaction - this phenomenon
is called molecular mimicry.
Bechterew: geassocieerd met HLA B27 allel. Chronisch ontstoken wervelkolom.
Figure 6 bechterew ontsteking
Graves: verhoogde schildklierfunctie (hyperthyreoidie) door antistoffen tegen
hormoonreceptor
Mantoux reactie: berust op IgG antistoffen tegen TB
Medische Microbiologie infectieziekten
Bacteriele groei fasen
o lag phase, bacteria adapt themselves to growth conditions. It is the period
where the individual bacteria are maturing and not yet able to divide.
o exponential phase, the number of new bacteria appearing per unit time is
proportional to the present population. This gives rise to the classic
exponential growth curve, in which the logarithm of the population
density rises linearly with time (see figure). The actual rate of this growth
(i.e. the slope of the line in the figure) depends upon the growth
conditions, which affect the frequency of cell division events and the
probability of both daughter cells surviving. Exponential growth cannot
continue indefinitely, however, because the medium is soon depleted of
nutrients.
o stationary phase, the growth rate slows as a result of nutrient depletion.
This phase is reached as the bacteria begin to exhaust the resources that
are available to them.
o death phase, bacteria run out of nutrients and die.
Haemophilus influenza. Ongekapselde vormen koloniseren mensen
(nasopharynx). Diagnose serologie. Invasieve infecties door stammen met
kapseltype B.
Influenzavirussen kunnen niet worden geserotypeerd ze hebben geen
celoppervlak. Meeste epidemieeen type A. Virulentie: Neuraminidase,
Hematoglutinen. Influenzavirus A is a genus of a family of viruses called
Orthomyxoviridae in virus classification. Influenzavirus A has only one species in
it; that species is called "Influenza A virus".
Rhinovirus are the most common viral infective agents in humans, and the causative
agent of the common cold. There are over 105 serologic virus types that cause cold
symptoms, and rhinoviruses are responsible for approximately 50% of all cases.
Serotype a group of microorganisms or viruses based on the cell surface antigens.
Serovars allow organisms to be classified at the sub-species level; an issue of
particular importance in epidemiology Serovars may be established based on
virulence factors, lipopolysaccharides in Gram-negative bacteria, presence of a
exotoxin (pertussis toxin in Bordetella pertussis, for example), plasmids, phages, or
other characteristic which differentiate two members of the same species.
Classificatie van bacterien door serotypering maakt gebruik van fenotypische
karakteristieken van bacterien.
Neisseria meningitidis meningitis
Neisseria spp commensaal in de oropharynx
Neisseria gonorroe (gonococcen) Ophtalmia neonatorum
Figure 7 intracellulaire neisseria diplococcen
Figure 8 neisseria meningitis
Chlamydia trachomatis: trachoma, conjunctivitis, pneumonie, uretritis; alles met
name bij neonaten. Heeft twee ontwikkelingsstadien.
Figure 9 cyclus chlamydia
Figure 10 conjunctivitis door chlamydia in het oog
Adenovirus Largest virus; can cause human infections ranging from respiratory
disease (mainly species HAdV-B and C), and conjunctivitis (HAdV-B and D), to
gastroenteritis (HAdV-F serotypes 40 and 41). Adenoviruses are unusually stable to
chemical or physical agents and adverse pH conditions, allowing for prolonged
survival outside of the body and water. Adenoviruses are primarily spread via
respiratory droplets, however they can be spread by fecal routes as well.
Figure 11 Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Atypische pneumonie: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; niet gevoelig voor Beta lactam
antibiotica. Zuurvast.
Shigellosis: Symptoms may range from mild abdominal discomfort to full-blown
dysentery characterised by cramps, diarrhea, fever, vomiting, blood, pus, or mucus
in stools or tenesmus. Onset time is 12 to 50 hours.
Lobulaire pneumonie: Streptococcus pneumoniae
Hepatitis A en B: preventie mogelijk met vaccinatie
DNA virussen: pokken, herpes, adeno, hepatitis B, papilloma, parvo
RNA virussen: mazelen, influenza, ebola, HIV, rhino, polio, rubella, yellow fever
RT-PCR is a one or two-step process for converting RNA to DNA and the
subsequent amplification of the reversely-transcribed DNA
Huidflora (zoals S. aureus) bestaat voornamelijk uit G+ bacterien.
S. aureus: EXOtoxine TSS en Scalded Skin Syndrome
Streptococcen: Bacteriele endocarditis, acuut reuma door Viridans strepto’s.
Sptrepto A (S. pyogenes) geeft pharyngitis. Onderscheiden op basis van hemolyse.
Individual species of Streptococcus are classified primarily based on their
hemolytic properties (breakdown of red blood cells in a lab).[2] Alpha hemolysis is
caused by a reduction of iron in hemoglobin giving it a greenish color on blood
agar. Beta hemolysis is complete rupture of red blood cells giving distinct, wide,
clear areas around bacterial colonies on blood agar. Lancefield serotyping - based
on specific carbohydrates in the bacterial cell wall - is used for further
characterizing the Beta hemolytic streptococcal species.[3] These are named
Lancefield groups A to O. Medically, Beta-hemolytic streptococci of Lancefield
groups A and B (also known as “Group A Strep” and “Group B Strep”) are the most
important. alpha-hemolytic streptococci (particularly S. pneumoniae and
Streptococcus Viridans-group) cause common diseases in man. Pneumococ
Kapsel bepalend voor serotype (galtest)
Obligaat intracellulair: Chlamydia, Mycobacterium leprae, Neisseria meningitidis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis kan intracellulair groeien
Immuniteit na infectie: na infecties Rhinovirussen, HAV
Self-limiting infecties: Campylobacter en Helicobacter gestro ent
Zoonose: Campylobacter (als Helicobacter)
O-antigeen: deel van het LPS (endotoxin) van Enterobacterien
o Lipid A
o Polysaccharide kern
o O-antigeen
Enterobacters: pathogene soorten niet in staat lactose om te zetten (test)
o Pathogeen: Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia
o Onschuldiger: E. coli, Klebsiella
Salmonella
o Zuurresistent
o Enteritis door celdood in darmwand
Salmonella typhi: Typhoid fever (or enteric fever) Vlekkentyfus is an illness
caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. Common worldwide, it is transmitted
by ingestion of food or water contaminated with feces from an infected person.[1]
The bacteria then multiply in the blood stream of the infected person and are
absorbed into the digestive tract and eliminated with the waste. Hoge koorts,
diarree.
Yersinia pestis: geen diarree
Rijstwaterdiarree: Vibrio cholerae
Mazelenvirus: couperen met cellulaire respons
Rubella: immuniteit moeder beschermt kind, enige gastheer is de mens; ‘Duitse
mazelen’ met exantheem
Urineweginfecties:
o S. saprophyticus bij jonge vrouwen
o E.coli de meeste gevallen 80%
Corpus alienum infecties: Stafylo epidermidis
Meningitis: bacterieel heeft slechtere progn dan viraal
Lyme disease or Lyme borreliosis is the most common vector-borne disease in the
Northern Hemisphere, and the most common tick-borne illness in the United States
and Europe. Named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, it is now one of the
fastest growing infectious diseases in the U.S. In the United States, Lyme disease is
most often acquired from the bite of the Ixodes scapularis tick, with the spirochete
Borrelia burgdorferi the only infecting organism
CMV Cytomegalovirus, is a genus of Herpes viruses; in humans the species is
known as Human herpesvirus 5 (HHV-5). It belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae
subfamily of Herpesviridae. The name means "cell very big virus". CMV especially
attacks salivary glands and may also be devastating or even fatal to fetuses. CMV
infection can also be life threatening for patients who are immunocompromised
(e.g. patients with HIV or organ transplant recipients).
Cholera: on reaching the intestinal wall, they start producing the toxic proteins
that give the infected person a watery diarrhea which carries the multiplying and
thriving new generations of V. cholerae bacteria out into the drinking water of the
next doomed persons
Legionella: reservoir in water
Duivenfeces: Cryptococcus neoformans
Figure 12 cryptococcose verwarring
Interferons (IFNs) are a class of natural proteins produced by the cells of the
immune system in response to challenges by foreign agents such as viruses,
bacteria, parasites and tumor cells. Interferons belong to the large class of
glycoproteins known as cytokines. Interferon-α is secreted by leukocytes (B-cells
and T-cells). Interferon-β is secreted by fibroblasts, and interferon-γ is secreted by
T-cells and natural killer lymphocytes. Several different forms of interferon alpha,
including interferon-alpha-2a, interferon-alpha-2b, and interferon-alfacon-1 are
approved for the treatment of viral hepatitis.
S. aureus: steenpuisten. Commensaal bij 30%
E. Coli: G- staven
Ziekenhuisinfectie: Alle infecties die worden opgelopen in het ZH, maar niet die al
daarvoor waren opgelopen.
Chlamydia trachomatis: genitale infectie kan symptoomloos zijn
Mazelen: Porte dentree luchtwegen, na infectie levenslange immuniteit
HBV: Chronische infectie verhoogt kans op leverkanker
HAV: vaccinatie beschikbaar, maar infectie niet behandelbaar
Mycosen: schimmels. Die van de huid beperken zich tot de hoornlaag
MM therapie
Antibiotica
peptidoglycaan De celwand van G- bacterien bevat weinig peptidoglycaan. Crosslinking van peptidoglycaan wordt gekatalyseerd door penicilin-binding proteins
(PBSs). Penicilin Binding Proteins (PBS) kunnen zich binden aan Lactamantibiotica
Kapsels Bij zowel G+ als G- bacterien kunnen kapsels de celwand bedekken.
Zowel G+ als G- bacterien produceren exotoxinen
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a large molecule that contains both lipid and a
carbohydrate. They are a major suprastructure of Gram-negative bacteria which
contributes greatly to the structural integrity of the bacteria, and protects them from
host immune defenses.Het core polysaccharide van LPS is soortspecifiek. Alleen Gbacterien bezitten lipopolysacchariden (LPSs). Lipid A is verantwoordelijk voor de
toxische effecten van LPS.
Coagulase is an adhesin (EC 3.4.23.48) produced by Staphylococcus aureus to
localize an area of residence that converts fibrinogen to fibrin. In laboratory, it is
used to distinguish between different types of Staphylococcus isolates. Coagulase
negativity excludes S. aureus. Maar het maakt geen onderscheid tussen Aureus en
Epidermidis
Plasmiden kunnen coderen voor eigenschappen die bacterien virulent maken (bv
via sex pili bij E. coli).
Virulence is either the relative pathogenicity or the relative ability to do damage to
the host of an infectious agent. The term is used mainly for viruses, but it can be
more generally applied to parasites or bacteria.
Beta lactamase inhibitors verstoren de biosynthese van peptidoglycaan; worden
meestal gebruikt in combinatie met andere penicilines
Aminoglycosiden De irreversibele binding van aminoglycosiden aan bacteriele
ribosomen leidt tot bacteriele celdood
Chlooramfenicol kan aplastische anemie veroorzaken
Clindamycine
o Aerobic gram-positive cocci, including some members of the
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus (eg. pneumococcus) genera.
o Anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, including some members of the
Bacteroides and Fusobacterium genera
Sulfonamiden zowel tegen G+ als G- bacterien
Aminoglycosides are a group of antibiotics that are effective against certain types
of bacteria. They include amikacin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, netilmicin,
paromomycin, streptomycin, tobramycin and apramycin. Those which are derived
from Streptomyces species are named with the suffix -mycin, while those which are
derived from micromonospora are named with the suffix -micin. Since they are not
absorbed from the gut, they are administered intravenously and intramuscularly
Tetracyclines remmen de groei van G+ en G- bacterien. It works by inhibiting
action of the prokaryotic 70S ribosome.
Antivirotica
Virion kan naast het virale genoom ook 1 of meer enzymen bevatten
Positive stranded RNA virussen Het genoom zelf fungeert in de gastheercel als
mRNA
Retrovirussen zoals HIV: RNA is de basis voor de synthese van viraal DNA. A
provirus is a retrovirus that has integrated itself into the DNA of a host cell. To do
this, the RNA of the retrovirus is transcribed into DNA by reverse transcriptase,
then inserted into the host genome by an integrase.
AZT Zidovudine (INN) or azidothymidine (AZT) (also called ZDV) is an
antiretroviral drug, the first one approved for treatment of HIV. Like other reverse
transcriptase inhibitors, AZT inhibits HIV replication by inhibiting the action of
reverse transcriptase. Behandeling van een zwangere met HIV met AZT
vermindert de verticale transmissie.
Peptidenanaloga zoals gp 120 en CD4 remmen de aanhechting van HIV aan de
celmembraan
Vertical transmission refers to transmission of an infection, such as HIV, hepatitis
B, or hepatitis C, from mother to child during the perinatal period, the period
immediately before and after birth.
Amantadine (1-aminoadamantane, sold as Symmetrel®) is an antiviral drug that
was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1976 for the treatment of
Influenzavirus A in adults.
Aciclovir is a guanine analogue antiviral drug used most commonly for the
treatment of herpes simplex virus infection. Aciclovir wordt niet gelyseerd door
Thymidine kinase, want:
Thymidine kinase is required for the action of many antiviral drugs.
Pleconaril blocks Rhinoviral attachment to the host-cell receptors by integrating
into the viral capsid cavities, which inhibits viral capsid uncoating. This finally
results in the inhibition of viral replication required for effective rhinoviral
pathogenesis.
Antimycotica
Schimmels kunnen seksueel en aseksueel voortplanten
Azolderivaten inhiberen de ergosterolbiosynthese van schimmels
Amfotericine B targets de ergosterol in schimmel celwanden
Quinolones (antibiotica) act by inhibiting the bacterial DNA gyrase and/or the
topoisomerase IV enzyme. This way they inhibit DNA replication and transcription.
Quinolones, and fluroquinolones alike, are bactericidal drugs, actively killing
bacteria. Quinolones can enter cells easily and therefore are often used to treat
intracellular pathogens such as Legionella pneumophila and Bacillus anthracis.
5-fluorocytosine interfereert niet met de synthese van ergosterol door schimmels,
maar hecht aan ribosomen?
Kindergeneeskunde
Mazelen Lage IgM titers, suggestief voor subklinische mazelen. Na 3-7 dagen:
gegeneraliseerd grofvlekkig exantheem (wegdrukbaar) Na 9-11 dagen:
Kopliksevlekken –verheven witte plekjes op wangslijmvlies
Waterpokken Varicella Zoster VZV casus secundair pneumonie agv H.
influenzae. Complicaties
o secundaire G+ infecties van de bultjes: Bacteriele superinfectie huid
(groep A streptococcen, stafylococcen)
o Encephalitis
o Cerebellaireataxie
o Pneumonie
o Hemorrhagischevaricella
o Meningitis, arthritis, glomerulonefritis, myocarditis
o hepatitis, Reye syndroom
Pneumonie effusie: antibiotica als < 1 cm dik en pH > 7.3 -- , thoraxdrains als > 1
cm dik en pH < 7.3
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis Uitgebreide crescentvorming Snelle
daling GFR ≥50% in periode van dagen -3 maanden Pathologische indeling
o Anti-GBM antilichamen10-40% ANCA pos
o Syndroom van Goodpasture; Anti-GMB ziekte
o Immuuncomplexvormingkunnen pANCApos zijn met MPO neg
o Postinfectieus; Henoch-Schönlein; IgAnefropathie;
membraanproliferatieveglomerulonefritisetc
o Pauci-immune 80-90% ANCA pos
o Wegener granulomatose; microscopische polyangiitis; renal-limited
necrotizing crescentic
o glomerulonephritis; Churg-Strausssyndrome
ANCA Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a plasma protein, an acute phase protein produced
by the liver. It should not be confused with C-peptide or Protein C.
UTI: G- bacteriën bij elk aantal; G+ bacetrien bij enige duizenden tonen UTI aan.
Post Streptokokken Glomerulo Nefritis; antilichamen gevormd tegen membranen
als gevolg van moleculaire mimicry
HUS hemolytic-uremic syndrome sikkelcellen
S. pyogenes (alfa hemolytisch) veroorzaakt:
o B cel Immuuncomplexen: post strepto GNF
o B cel Antistoffen: artritis, carditis, chorea
o T cel cytokinen: toxic shock TSS
o Metastatische verspreiding: artritis, meningitis
o Enzymen: erysipelas, cellulitis
Chorea sancti viti (Latin for "St. Vitus' dance") is an abnormal voluntary
movement disorder, one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias.
IgA deficientie In the absence of normal IgA, the body can develop an immune
response against IgA itself, which can lead to severe reactions including
anaphylaxis to blood transfusions. Specifieke voorzargsmaatregelen nemen. Komt
niet zelden voor!
Perinatale infectie During childbirth, the infant is exposed to maternal blood and
body fluids without the placental barrier intervening and to the maternal genital
tract. Because of this, microorganism transmitted by blood (Hepatitis B, HIV),
organisms associated with sexually transmitted disease (Neisseria gonorrhoeae and
Chlamydia trachomatis), and normal flora of the genito-urinary tract are among
those commonly seen in infection of the newborn.
Intra-uterine infecties Bij moeder symptoomloos. Onder de gevolgen is
dysmaturiteit en hersenbeschadiging. More than 130 different bacterial species
may be involved. Ook Herpes simplex.
JCA Juvenile Chronische Artritis Definitie voor diagnose moet bestaan langer dan
3 maanden
SLE kan door placenta. Tegenwoordig grootste doodsoorzaak infecties door
behandeling
Allergische vasculitis huidbloedinkjes en gewrichtsklachten
Roodvonk: Streptokok complicaties GNF en acuut reuma
S aureus: skalded skin syndrome, TSS
Streptokokken: TSS
Exanthemen:
o Grofvlekkig exantheem, koplikse vlekken: mazelen
o Erythemateus exantheem: virussen
o Vesicobulleus: Herpes
o Malucopopuleus: Rubella
o Scarlatina is an exotoxin-mediated disease caused by Group A
streptococcal infection that occurs most often in association with a sore
throat and rarely with impetigo or other streptococcal infections.
o Exanthem subitum (meaning sudden rash), also referred to as roseola
infantum (or rose rash of infants), sixth disease and (confusingly) baby
measles, is a benign disease of children, generally under two years old,
whose manifestations are usually limited to a transient rash ("exanthum")
that occurs following a fever of about three day's duration.Until recently,
its cause was unknown: it is now known to be caused by two human
herpesviruses, HHV-6 and HHV-7, also called Roseolovirus. De
ziekteverschijnselen bestaan uit een vrij plots optredende, enige dagen
durende hoge koorts, (39 tot 40,5 °C), meestal zonder duidelijke
lokaliserende symptomen zoals oorpijn of een zere keel. De koorts zakt
dan vrij abrupt waarna het kind een uitslag ontwikkelt. Soms gaat de
uitslag gepaard met keelontsteking, oorontsteking en/of vergroting van de
lymfeklieren in hals en nek. Zodra de koorts zakt verschijnen de rozerode
tot paarse vlekjes over het gehele lichaam. Het kind hoeft geen erg zieke
indruk te maken en een koortswerend middel zoals paracetamol is meestal
reeds voldoende. Kenmerkend is optreden van leucopenie.
Figure 13 erythemateus exantheem door virussen
Figure 14 morbiliforme uitslag
Figure 15 scarlatina
Figure 16 varicella vesicobulleus
Figure 17 rubella; maculopopular rash
Figure 18 roseola
Figure 19 erythema marginatum: acuut reuma
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a rare chronic, progressive
encephalitis that affects primarily children and young adults, caused by the wild
measles virus. 1 in 100,000 people infected with measles are at risk. Incidentie
verlaagd door vaccinatie met BMR
Pyogenic refers to bacterial infections that make pus
Acuut reuma: diagnose + indien chorea en erythema marginatum wordt gevonden
Immuunvoorziening foetus: In de eerste 2 maanden beschermd tegen pyogene
infecties door moederlijke antistoffen. MAAR De antistofrespons tegen
polysacchariden komt pas na 18 maanden voldoende op gang
Coombs test If either alloimmunity or autoimmunity is directed against red blood
cells (RBCs), the direct Coombs test is positive
Kawasaki disease, also known as mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome,
mucocutaneous lymph node disease, infantile polyarteritis and Kawasaki
syndrome, is a poorly understood self-limited vasculitis that affects many organs,
including the skin and mucous membranes, lymph nodes, blood vessel walls, and
the heart.Kan op klinische gronden gediagostiseerd.
Figure 20 kawasaki disease
Coeliakie of glutenenteropathie (ICD-10 K90.0), ook wel inheemse spruw
genoemd is een aangeboren glutenintolerantie, waarschijnlijk veroorzaakt door een
immunologische reactie tegen gluten.
Hemolytische anemie: Auto-immuun: normochroom microcytair
Vasculitiden: In medicine, vasculitis (plural: vasculitides) is a group of diseases
featuring inflammation of the wall of blood vessels due to leukocyte migration
and resultant damage. While most vasculitides are rare, they generally affect
several organ systems and can cause severe disability. Vasculitiden kunnen worden
veroorzaakt door infectieziekten en een auto-immuunziekte veroorzaken (een falend
immuunsysteem). Nieren het vaakst betrokken
Rode hond: lymfkliervergroting retroauriculair, conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis: mazelen en rode hond
Inwendige
Pathognomonic characteristic or diagnostic for a particular disease
Purpura fulminans (PF) is a haemorrhagic condition usually associated with sepsis
or previous infection. Features include tissue necrosis, small vessel thrombosis
and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Gram-negative organisms are the
commonest cause of the acute infectious type, which is often associated with multiorgan failure. An idiopathic variety, however, is often confined to the skin. The
mortality rate has decreased with better treatment of secondary infections,
supportive care and new treatments, but it remains a disabling condition often
requiring major amputations. NIET specifiek (pathognomonisch) voor
meningokokkensepsis, maar kan een gevolg zijn
Figure 21 purpura fulminans
HIV: response op therapie niet beter als viral load lager is. Wordt niet gekenmerkt
door opp infecties (dit is AIDS)
Vragen
Ig klassen onderscheidt men op basis van ... ?
Het isotype van een antilichaam wordt bepaald door ...?
De HEV in de lymfeklier vervoeren ....?
5-fluorocytosine interfereert niet met de synthese van ergosterol door schimmels,
maar …?
Verbeteringen in transplantatie wschl door immuunsuppressie en tolerantie inductie
GVHD vooral bij beenmerg transplant












