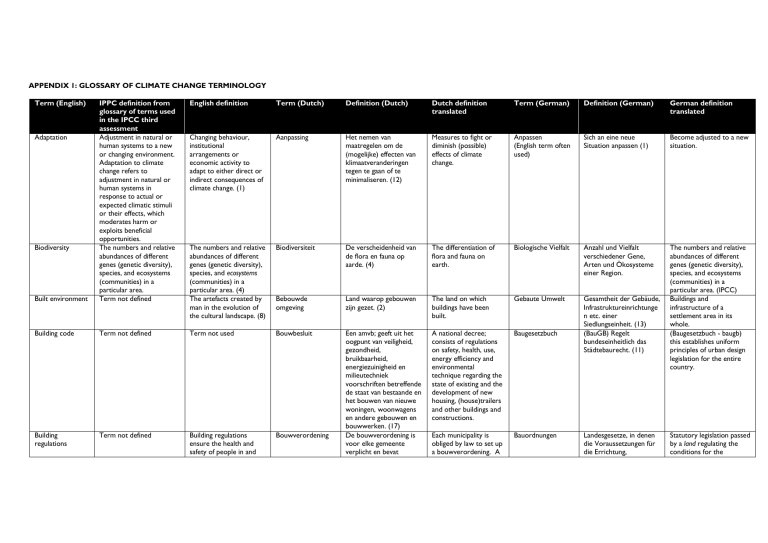
APPENDIX 1: GLOSSARY OF CLIMATE CHANGE TERMINOLOGY
Term (English)
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Changing behaviour,
institutional
arrangements or
economic activity to
adapt to either direct or
indirect consequences of
climate change. (1)
Aanpassing
Het nemen van
maatregelen om de
(mogelijke) effecten van
klimaatveranderingen
tegen te gaan of te
minimaliseren. (12)
Measures to fight or
diminish (possible)
effects of climate
change.
Anpassen
(English term often
used)
Sich an eine neue
Situation anpassen (1)
Become adjusted to a new
situation.
The numbers and relative
abundances of different
genes (genetic diversity),
species, and ecosystems
(communities) in a
particular area. (4)
The artefacts created by
man in the evolution of
the cultural landscape. (8)
Biodiversiteit
De verscheidenheid van
de flora en fauna op
aarde. (4)
The differentiation of
flora and fauna on
earth.
Biologische Vielfalt
Anzahl und Vielfalt
verschiedener Gene,
Arten und Ökosysteme
einer Region.
Built environment
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Adjustment in natural or
human systems to a new
or changing environment.
Adaptation to climate
change refers to
adjustment in natural or
human systems in
response to actual or
expected climatic stimuli
or their effects, which
moderates harm or
exploits beneficial
opportunities.
The numbers and relative
abundances of different
genes (genetic diversity),
species, and ecosystems
(communities) in a
particular area.
Term not defined
Bebouwde
omgeving
Land waarop gebouwen
zijn gezet. (2)
The land on which
buildings have been
built.
Gebaute Umwelt
Building code
Term not defined
Term not used
Bouwbesluit
A national decree;
consists of regulations
on safety, health, use,
energy efficiency and
environmental
technique regarding the
state of existing and the
development of new
housing, (house)trailers
and other buildings and
constructions.
Baugesetzbuch
Building
regulations
Term not defined
Building regulations
ensure the health and
safety of people in and
Bouwverordening
Een amvb; geeft uit het
oogpunt van veiligheid,
gezondheid,
bruikbaarheid,
energiezuinigheid en
milieutechniek
voorschriften betreffende
de staat van bestaande en
het bouwen van nieuwe
woningen, woonwagens
en andere gebouwen en
bouwwerken. (17)
De bouwverordening is
voor elke gemeente
verplicht en bevat
Gesamtheit der Gebäude,
Infrastruktureinrichtunge
n etc. einer
Siedlungseinheit. (13)
(BauGB) Regelt
bundeseinheitlich das
Städtebaurecht. (11)
The numbers and relative
abundances of different
genes (genetic diversity),
species, and ecosystems
(communities) in a
particular area. (IPCC)
Buildings and
infrastructure of a
settlement area in its
whole.
(Baugesetzbuch - baugb)
this establishes uniform
principles of urban design
legislation for the entire
country.
Each municipality is
obliged by law to set up
a bouwverordening. A
Bauordnungen
Adaptation
Biodiversity
Landesgesetze, in denen
die Voraussetzungen für
die Errichtung,
Statutory legislation passed
by a land regulating the
conditions for the
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
around buildings by
providing functional
requirements for building
design and construction.
The regulations also
promote energy
efficiency in buildings.
Carbon storage
Term not defined
Catchment
Term not defined
Climate
Climate in a narrow sense
is usually defined as the
‘average weather’ or more
rigorously as the statistical
description in terms of the
mean and variability of
relevant quantities over a
period of time ranging
from months to thousands
or millions of years. The
classical period is 30 years,
as defined by the world
meteorological
organisation (WMO).
These relevant quantities
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
voorschriften omtrent
bouw, maten, gebruik en
sloop van woningen,
gebouwen en andere
bouwwerken en
voorschriften omtrent
staat van open erven en
terreinen. (17)
bouwverordening
consists of regulations
on building,
measurements, use and
destruction of housing,
buildings and other
constructions and
regulations on the state
of public grounds and
terrains.
Part of the global
carbon cycle; the long
term storage of carbon
in biomass,
underground/soil and in
products (e.g. through
cutting down forests).
The long-term storage of
carbon or CO2 in the
forests, soils, ocean, or
underground in depleted
oil and gas reservoirs,
coal seams, and saline
aquifers. Also referred
to as engineered carbon
sequestration. Carbon
capture and storage can
be referred to as CCS.
(3)
An area that collects and
drains rainwater. (4)
Koolstofvastlegging
Onderdeel van de
mondiale
koolstofkringloop; the
lange termijn vastlegging
van koolstof in de
biomassa, in de bodem
en in de producten (bijv.
via het kappen van
bossen). (18)
Stroomgebied
Climate refers to the
average weather
experienced in a region
over a long period,
typically 30 years. This
includes not just
temperature, but also
wind and rainfall patterns.
The climate of the earth
is not static, and has
changed many times in
the past in response to a
variety of natural causes
(from www.ukcip.co.uk).
Klimaat
Een gebied dat
regenwater afwatert naar
een specifieke rivier. (13)
Gemiddelde van het
weer, d.w.z.
Gemiddelden van
temperatuur,
vochtigheidsgraad,
luchtdruk, wind
bewolking en neerslag.
(1)(2)(3)
An area that discharges
its rainwater on a
specific river.
Means of weather, i.e.
means of temperature,
humidity, air pressure,
wind, cloudiness and
precipitation.
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Änderung und den
Abbruch baulicher
Anlagen geregelt sind.
(11)
construction, alteration
and demolition of built
structures.
Absorptionsflächen
Frei- und Grünflächen
mit klimatischer
Funktion. In Abhängigkeit
von ihrer Beschaffenheit
und Vegetation werden
auf diesen Flächen
Kohlendioxid in
Sauerstoff umgewandelt,
Schwebstaub gebunden
und Strahlen gefiltert. (4)
Green areas with climatic
function. Depending on
their structure and
vegetation these areas can
convert CO2 into oxygen,
they can bind dust and
filter rays.
Flusseinzugsgebiet
Fläche aus der sich ein
Fluss speist. (6)
Area from which a river
gets its water.
Klima
Gesamtheit der
Wetterphänomene. (1)
Weather in its entirety.
Term (English)
Climate change
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
are most often surface
variables such as
temperature, precipitation
and wind.
Climate change refers to a
statistically significant
variation in either the
mean state of the climate
or in its variability,
persisting for an extended
period (typically decades
or longer). Climate
change may be due to
natural internal processes
or external forcings, or to
persistent anthropogenic
changes in the
composition of the
atmosphere or in land use.
Note that the UNFCC
defines ‘climate change as:
‘a change of climate which
is attributed directly or
indirectly to human activity
that alters the composition
of the global atmosphere
and which is in addition to
natural climate variability
observed over comparable
time periods’. The
UNFCC thus makes a
distinction between
‘climate change’
attributable to human
activities altering the
atmospheric composition,
and ‘climate variability’
attributable to natural
causes.
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
The term "climate
change" usually refers to
recent changes in climate
that have been observed
since the early 1900’s
(from www.ukcip.co.uk).
Klimaat-verandering
Verandering van het
gemiddelde weer.
(1)(2)(3)
Change of the mean
weather.
Klimawandel
Grundlegender Wandel
des Wetters. (1)
Fundamental change of
mean weather.
Term (English)
Climate change
impact
Climate
prediction
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Consequences of climate
change on natural and
human systems.
Depending on the
consideration of
adaptation, one can
distinguish between
potential impacts and
residual impacts. Potential
impacts: all impacts that ay
occur given a projected
change in climate, without
considering adaptation.
Residual impacts: the
impacts of climate change
that would occur after
adaptation.
A climate prediction or
climate forecast is the
result of an attempt to
produce a most likely
description or estimate of
the actual evolution of the
climate in the future (e.g.
at seasonal, interannual, or
long-term time-scales).
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
The effects on the
physical environment,
ecosystems, individual
species and societies
from changes in the
climate.
Effecten van
klimaatverandering
Effecten van de
veranderingen in het
klimaat op de zeespiegel,
ecosystemen en drainage
regimes van rivieren en
hun effecten op
landbouw, burgers,
industrie en scheepvaart.
(3)
Effects of changes in
climate on the sea level,
ecosystems and
drainage regimes of
rivers, in turn affecting
agriculture, civilians,
industry and shipping.
Auswirkungen des
Klimawandels
Auswirkungen des
Klimawandels auf die
Stabilität der physische
Umwelt, von
Ökosystemen und
Gesellschaften.
The effects on the physical
environment, ecosystems,
individual species and
societies from changes in
the climate.
An extrapolation or
projection of the state of
a system, or value of a
variable, based on
available knowledge or
information and defined
assumptions. Forecasts
are usually either
temporal and/or spatial
extrapolations.
Temporal extrapolations
can be forward (forecast)
or backward (hindcast).
Where uncertainty can
be estimated and a level
of confidence can be
assigned to a climate or
other projection, it
becomes a forecast or
prediction. (2)
Klimaat
voorspelling (term
not widely used)
Een extrapolatie of
projectie van de staat van
een system, of waarde
van een variabele,
gebaseerd op
beschikbare kennis of
informatie en aannames.
Voorspellingen zijn
meestal ofwel
extrapolaties in de tijd of
in ruimte. Extrapolaties in
de tijd kunnen
vooruitblikken of
terugblikken. Wanneer
de onzekerheid ingeschat
kan worden en een
bepaald niveau van
betrouwbaarheid
gekoppeld kan worden
aan een klimaat of
andersoortige prognose,
dan wordt het een
voorspelling. (Term
(Term translated from
English definition).
Klimavorhersage
Die Klimavorhersage
oder Klimaprognose
beschreibt die
wahrscheinlichste
Veränderung des Klimas
in der Zukunft, z.B. in
Bezug auf saisonale,
jährliche oder
längerfristige
Zeitschienen.
A climate prediction or
climate forecast is the
result of an attempt to
produce a most likely
description of the actual
evolution of the climate in
the future (e.g. at seasonal,
inter annual, or long-term
time-scales). (IPCC)
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
translated from English
definition)
Climate
projection
Climate change
scenario
A projection of the
response of the climate
system to emission or
concentration scenarios of
greenhouse gases and
aerosols, or radiative
forcing scenarios, often
based upon simulations by
climate models. Climate
projections are
distinguished from climate
predictions in order to
emphasize that climate
projections depend upon
the
emission/concentration/
radiative forcing scenario
used, which are based on
assumptions, concerning,
for example, future socioeconomic and
technological
developments that may or
may not be realised, and
are therefore subject to
substantial uncertainty.
A plausible and often
simplified representation
of the future climate,
based on an internally
consistent set of
climatological
relationships, that has
been constructed for
explicit use in investigating
the potential
consequences of
A potential future
evolution of a quantity or
set of quantities, often
computed with the aid of
a model. Projections are
distinguished from
‘predictions’ in order to
emphasise that
projections involve
assumptions concerning,
for example, future
social-economic and
technological
developments that may
or may not be realised.
(4)
Prognose
Voorspelling over wat er
in de toekomst gaat
gebeuren. (16)
Prediction about what
will happen in the
future.
Prognose
Vorhersage zu
zukünftigen
Ereignissen(1)
Prediction about what will
happen in the future.
A coherent and
internally-consistent
description of the change
in climate by a certain
time in the future, using a
specific modelling
technique and under
specific assumptions
about the growth of
greenhouse gas and
other emissions and
Scenario
Mogelijke
ontwikkelingslijn. (16)
Possible way in which
the climate will develop.
Szenario
Entwicklungsmöglichkeite
n. (1)
Possible way in which the
climate will develop.
Term (English)
Climate research
CO2 emissions
CO2 equivalent
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
anthropogenic climate
change, often serving as
input to impact models.
Climate projections often
serve as the raw material
for constructing climate
scenarios, but climate
scenarios usually require
additional information such
as about the observed
current climate. A
‘climate change scenario’ is
the difference between a
climate scenario and the
current climate.
Term not defined
A naturally occurring gas,
and also a by-product of
burning fossil fuels and
biomass, as well as landuse changes and other
industrial processes. It is
the principal
anthropogenic greenhouse
gas that affects the earth’s
radiative balance. It is the
reference gas against
which other greenhouse
gases are measured and
therefore has a global
warming potential of 1.
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Scientific inquiry aimed at
the discovery,
interpretation,
reinterpretation or
application of the past,
current and future
climate conditions. (8)
The release of carbon
dioxide into the
atmosphere. (5)
Klimaat-onderzoek
Onderzoek naar de
ontwikkeling van het
gemiddelde weer.(1)
Research on the
development of mean
weather.
Klimaforschung
Erforschung des Wetters.
(1)
Research on the
development of mean
weather.
CO2 - emissies
Uitstoot van het
broeikasgas kooldioxide.
(2)(3)
Emission of the
greenhouse gas carbon
dioxide.
CO2 Emission
Emissionen des
Treibhausgases CO2. (1)
Emission of the
greenhouse gas carbon
dioxide.
The quantity of a given
GHG multiplied by its
global warming potential.
CO2 equivalent
Een CO2-equivalent
(CO2-eq.) Is een
rekeneenheid om de
A CO2-equivalent is a
unit of account to
compare the
CO2-Äquivalente
Angabe der
Konzentration eines
Gases bezogen auf seine
The concentration of a gas
in relation to its green
house effectiveness
about other factors that
may influence climate in
the future. (1)(2)
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
This is the standard unit
for comparing the degree
of harm which can be
caused by emissions of
different GHGs. (from
http://www.ghgprotocol.
org/glossary.htm)
Coastal defence
Term not defined
A defence system is two
or more defences acting
to achieve common goals
(e.g. maintaining flood
Protection to a single
flood cell community).
Kust-verdediging
Coastal erosion
Term not defined
Kusterosie
Coastline
Term not defined
The actions of marine
waves, through their
fourfold processes of
hydraulic action,
corrasion, attrition and
solution, when they
combine to attack the
coastline, thereby causing
it to retreat.
The line forming the
boundary between the
land and the water.
More specifically,
‘coastline’ refers to the
highest limit reached by
the swash of storm
waves during high-water
spring tides. (8)
Kustlijn
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
bijdrage van
broeikasgassen aan het
broeikaseffect onderling
te kunnen vergelijken.
Het is gebaseerd op het
global warming potential
(gwp), de mate waarin
een gas bijdraagt aan het
broeikaseffect. (19)
contribution of
greenhouse gases to the
greenhouse effect. It is
based on the global
warming potential
(GWP), the amount in
which a gas contributes
to the greenhouse
effect.
Verdedigingssysteem
langs de kust die gebruikt
wordt om het
achterliggende land te
beschermen; verdediging
kan hard (in de vorm van
steen, basalt,
betonblokken) of zacht
(zand en duinen) zijn.
(10)
Proces waarbij de kustlijn
onder invloed van wind
en water (langzaam maar
gestaag) achteruitgaat.
(10)
Defence system along
the coast, to protect
the land behind it:
defence can be hard (in
form of stones, basalt
or concrete blocks) or
soft (sand and dunes).
Grens tussen land en zee;
meestal de gemiddelde
waterlijn. (10)
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Treibhauswirksamkeit im
Vergleich zu CO2 als
Referenzsubstanz
(CO2=1 ). (4)
compared with co 2 as a
reference (CO2=1).
Küstenschutz
Maßnahmen zum Schutz
von Küstenzonen gegen
Hochwasser. (1)
Measures for the
protection of coastal
areas.
Process in which the
coast line moves
backwards (slowly but
steadily) under influence
of wind and water.
Küstenerosion
Verlagerung von
Bodenmaterial entlang
einer Küstenlinie durch
Meeresströmungen und
Sturmfluten. (4)
The movement of ground
material along a coastline
caused by ocean current
and storm tides.
Boundary between land
and sea.
Küstenlinie
Grenzbereich zwischen
Meer und Land. (1)
Area where sea and land
meet.
Term (English)
Cultural heritage
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Term not defined
Drainage
Term not defined
Drainage basin
Term not defined
Drought
Term not defined
Dyke ring
Term not defined
Dyke
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
The legacy of historic
features resulting from
man’s activities e.g. the
historic dimension of the
landscape including rural
and urban settlement
patterns, and historic and
archaeological
features/monuments.
The process by which
water is discharged from
an area by a river. (8)
Cultuur historisch
waardevol
landschap of
element
Valuable structures or
elements in the form of
soil, built environment
or landscape that reflect
the impacts of human
or natural forces in a
characteristic way.
Kulturelles Erbe
Gesamtheit der
spezifischen kulturellen
Errungenschaften einer
Gesellschaft.
Totality of the specific
cultural achievements of a
society.
Discharge or surplus
(ground)water from an
area via underground
waterways to a river.
Abfluss
Wassermenge die ein
Fluss in einer Zeiteinheit
durchfließen kann. (6)
Amount of water that can
run through a river in a
given time unit.
The part of the land
surface which is drained
by a unitary river system.
Its perimeter is marked
by a drainage divide or
watershed. (8)
An extended period of
dry weather; extreme
dryness due to lack of
rain. (8)
Term not used
Stroomgebied
Waardevolle structuren
of elementen in de vorm
van bodem, gebouwde
omgeving of landschap,
die de impact van
menselijke of natuurlijke
krachten op een
karakteristieke wijze
weergeven. (12)(13)
Afvoer van overtollig
(grond)water uit een
gebied door middel van
ondergrondse
watergangen naar een
rivier. (13)
Een gebied dat
regenwater afwatert naar
een specifieke rivier. (13)
An area that discharges
its rainwater on a
specific river.
Einzugsgebiet
Gebiet aus dem ein Fluß
mit Wasser gespeist
wird. (6)
Area that feeds a river
with water.
Droogte
Gebrek aan water;
watertekort. (5)
Lack of water; water
shortage.
Trockenheit, Dürre
Aussergewöhnliche
Trockenheit durch
ausbleibende Regenfälle.
Unusual dryness caused
e.g. by absence of rainfalls.
Dijkring
Dijken
System of dams and
dykes that encloses a
dyke ring area.
Construction that helps
to protect the land
behind it against water.
Ringdeich
An artificial embankment
or excavated drainage
ditch constructed to
prevent marine flooding
of coastal lowlands. (8)
Stelsel van waterkeringen
dat een dijkringgebied
omsluit. (13)
Bouwwerk te
bescherming van het
achterliggende land tegen
water.(10)
Deichsystem, das ein
begenztes Gebiet
ringförmig umschließt.
Erdwall zum Schutz von
Küsten und
Flußlandschaften vor
Überflutungen. (14)
System of dams and dykes
that encloses a dyke ring
area.
Earth embankment for the
protection of coastal and
river areas against
flooding.
Drainage
Deich
Term (English)
Ecological
corridor
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Ecological corridors link
habitats together and
allow the
movement/migration of
habitats and species.
Ecologische
verbindings-zone
Gebieden die kern- en
natuurontwikkelingsgebie
den aan elkaar knopen;
zijn belangrijk om de
verspreiding van en
contacten tussen dieren
en planten te verbeteren.
(12)
Een samenhangend
netwerk van bestaande
en nog te ontwikkelen
belangrijke
natuurgebieden. De
ecologische
hoofdstructuur is
opgebouwd uit
kerngebieden,
natuurontwikkelingsgebie
den en verbindingszones.
(12)
Het samenleven van
planten en diersoorten in
een bepaalde omgeving.
(4)
Ecological corridors are
areas that connect
core- and nature
development areas.
These are of great
importance to improve
the movement of
animals and plants.
The ecological main
structure is an
integrated network of
existing and still to be
developed important
natural areas. The
ecological main
structure consists of
core areas, nature
development areas and
corridor zones.
Biotopverbund
Verbund zwischen
verschiedenen Biotopen,
die einen Austausch, die
Wanderung von Arten
ermöglicht. (1)
Connection between two
or more natural areas to
make it possible for flora
and fauna to migrate.
The cohabitation of
plants and animals in a
given environment.
Ökosystem
Natürliche Einheit von
Lebendem und seinem
Lebensraum. (6)
System connecting flora
and fauna in their specific
environment.
Reductie van emissie van
CO2 en niet-CO2
broeikasgassen door
bevorderen energie
besparing, beperken
koolstofintensiteit van
Reduction of emission
of CO2 and non-CO2
greenhouse gases by
enhancing energy
savings, diminishing
carbon intensity of fuels
Emissionsminderun
g
Reduktion des
Ausstosses von Abgasen.
(6)
Reduction in the output of
exhaust fumes.
Ecologische
hoofdstruc-tuur
Ecosystem
Emission
reduction
A system of interacting
living organisms together
with their physical
environment. The
boundaries of what could
be called an ecosystem are
somewhat arbitrary,
depending on the focus of
interest or study. Thus,
the extent of an
ecosystem may range from
very small spatial scales to,
ultimately, the entire
earth.
Term not defined
A system of
interconnected habitats
and their species of flora
(plants) and fauna
(animals), usually defined
by a specific geographical
area and/or climatic
regime, e.g. mountain,
polar, forest ecosystem.
(5)
Ecosysteem
Reduction in greenhouse
gas emissions from
vehicles, industrial
processes, agriculture,
etc.
Emissie reductie
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Emissions trading
A market-based approach
to achieving environmental
objectives that allows
those reducing greenhouse
gas emissions below what
is required, to use or
trade the excess
reductions to offset
emissions at another
source inside or outside
the country. In general,
trading can occur at the
intracompany, domestic,
and international levels.
See IPPC definition.
Emissiehandel
Energy efficiency
Ratio of energy output of a
conversion process or of a
system to its energy input.
Efficiënt energiegebruik
Extreme
(weather) event
An extreme weather event
is an event that is rare
within its statistical
reference distribution at a
particular place.
Definitions of ‘rare’ vary,
Careful use of energy,
with minimum wastage,
in buildings, industrial
processes, etc.
An event that is rare
within its statistical
reference distribution at a
particular place.
Definitions of ‘rare’ vary,
but an extreme event
Weersextremen
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
brandstof en bevorderen
gebruik van
hernieuwbare
energiebronnen. (3)
Emissiehandel is de
handel in emissierechten.
Emissierechten geven
landen of bedrijven het
recht geven om bepaalde
broeikasgassen of andere
schadelijke gassen uit te
stoten. Meer officieel is
emissiehandel de handel
in emissieruimte. De
emissieruimte geeft aan
hoeveel een land of
bedrijf van een bepaald
gas mag uitstoten
(emitteren). Het
systeem is flexibel: landen
en bedrijven kunnen
emissierechten kopen of
verkopen.bij
emissiehandel moeten
emissies door
emissierechten worden
gedekt: een land of
bedrijf moet voldoende
rechten hebben voor zijn
uitstoot. (20)
Een doordacht gebruik
van energie, niet meer
gebruiken dan
noodzakelijk. (2)(3)
Een weersextreme is een
weerssituatie die
statistisch gezien
zeldzaam is.
Klimaatveranderingen
maken dat deze
and enhancing use of
renewable energy
sources.
Emissions trading is the
trade in emission rights.
Emission rights give
countries or companies
the right to emit certain
greenhouse gases or
other harmful gases.
More officially emissions
trading is the trade in
emission space. The
emission space defines
how much of a certain
gas a country or
company is allowed to
emit. The system is
flexible; the rights and
space can be bought or
sold. When emission
trading takes place,
emissions have to be
covered by emission
rights: a country or
company has to have
sufficient rights for its
emissions.
Emissionshandel
Mart-Prinzip mit dem
umweltpolitische Ziele
erreicht werden sollen.
Marktteilnahmer können
notwendige CO2
Reduktionen bei anderen
Emittenden im In- oder
Ausland kaufen, die das
notwendige Maß an
Emissionsreduktionen
günstiger erzielen
können.
A market-based approach
to achieving environmental
objectives that allows
those reducing greenhouse
gas emissions below what
is required to use or trade
the excess (übermaß)
reductions to offset
(ausgleichen) reductions at
another source inside or
outside the country.
A wise and responsible
use of energy; not more
than necessary.
Effiziente Energie
Nutzung
Geringer Energieeinsatz
bei möglichst hohem
Wirkungsgrad. (6)
A wise and responsible use
of energy; not more than
necessary.
A weather extreme is a
weather event that is
statistically rare.
Climate changes
enhance the occurrence
of these extremes.
Extremereigniss
Wetterereignisse
ausserhalb normaler
Schwankungen. (5)
Weather phenomena
beyond the scale of normal
variation.
Term (English)
Flood
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
but an extreme weather
event would normally be
as rare as or rarer than
the 10th or 90th percentile.
By definition, the
characteristics of what is
called extreme weather
may vary from place to
place. An extreme climate
event is an average of a
number of weather events
over a certain period of
time, an average which is
itself extreme (e.g. rainfall
over a season).
Term not defined
Flood area/flood
plain
Term not defined
Flood risk
management
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
would normally be as rare
as or rarer than the 10th
or 90th percentile. (4)
Overflowing of a body of
water, especially onto
normally dry land. (7)
The part of a river valley,
adjacent to the channel,
over which a river flows
in times of flood. It is a
zone of low relief and
gentle gradients and may
incorporate oxbow lakes,
point bars, abandoned
channels, scrolls, all
indicative of the fact that
the river has shifted its
position continuously
during the present
regime of the stream. (8)
Flood risk management
activities can reduce the
probability of flooding
through the management
of land, river systems and
flood defences, and
reduce the impact of
floods through effective
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Het buiten de oevers
treden van waterwegen.
(10)
Een retentiegebied of
retentiebekken is
binnendijks gebied, dat bij
hoogwater gebruikt kan
worden om water
tijdelijk op te vangen.
(21)
The overflowing of a
river.
Überflutung
A retention area or
retention basin is an
area on the landside of
the dykes, that in case
of high water can be
used to temporarily
store water.
Überschwemmungs
gebiete
Hochwasser das
Landstriche unter
Wasser setzt. (1)
Gebiete die im Fall von
extremem Hochwasser
geflutet werden können.
(6)
An overflow of large
amount of water over dry
land.
Areas that can be flooded
in case of extreme high
levels to lower the flood
peak.
Hoogwaterbescherming
heeft tot doel de
veiligheid te verhogen
door te anticiperen in
plaats van reageren op
wateroverlast. Dit
gebeurt in het bijzonder
door het creëren van
High water protection
aims at enlarging safety
by anticipating instead
of reacting to water
problems. This
especially happens
through creating more
”moving space” for
Vorbeugender
Hochwasserschutz
Der vorbeugende
Hochwasserschutz
koordiniert sektorale
Planungen
(Wasserwirtschaft,
Flußausbau, Stadt- und
Regionalplanung,
internationale
‘Preventive flood
protection’ coordinates
sectoral planning such as
water management, spatial
and regional planning,
international cooperation,
as well as the different
administrative levels (state,
extremen vaker
voorkomen. (1)
Overstroming
Retentiegebied
Hoogwaterbescher
ming
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
land use planning,
regulation, flood warning
and emergency response.
(from environment
agency
Strategy for flood risk
management
(2003/4 - 2007/8))
Greenhouse effect
Greenhouse gases
effectively absorb infrared
radiation, emitted by the
earth’s surface, by the
atmosphere itself due to
the same gases, and by
clouds. Atmospheric
radiation is emitted to all
sides, including downward
to the earth’s surface.
Thus greenhouse gases
trap heat within the
surface-troposphere
system. This is called the
‘natural greenhouse effect’.
Atmospheric radiation is
strongly coupled to the
temperature of the level at
which it is emitted. In the
troposphere, the
temperature generally
decreases with height.
Effectively, infrared
radiation emitted to space
originates from an altitude
with a temperature of, on
average, -19c, in balance
with the net incoming
A term used to describe
the effect where
greenhouse gases trap reemitted infrared
radiation, so heating up
the atmosphere. This is a
natural phenomenon and
increases the earth’s
average temperature
from -18c to +15c.
This should not be
confused with the
enhanced greenhouse
effect, the increase of the
greenhouse effect as a
result of human activities.
(5)
Broeikas-effect
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
meer beweegruimte voor
water. Maatregelen
houden onder andere in
het verleggen van dijken,
afgraven van
uiterwaarden, aanleggen
van retentiegebieden en
graven van nevengeulen.
Ruimtelijke kwaliteit
speelt een belangrijke rol
in het uitvoeren van deze
maatregelen. (21)
Stijging van de
temperatuur door een
teveel aan broeikasgassen
in de atmosfeer, welke
het gevolg is van een
door menselijke activiteit
veroorzaakte verstoring
van het natuurlijke
proces, waarin een aantal
gassen in de atmosfeer
het invallende licht van
de zon doorlaten en de
door de aarde
teruggekaatste infrarode
(warmte)straling
absorberen en deze
warmte gedeeltelijk weer
terugkaatsen naar het
aardoppervlak. (2)(3)(4)
water. Measures are
moving dykes, digging
up river foreland,
developing retention
areas and digging up
additional channels
along rivers. Spatial
quality plays an
important role in
executing these
measures.
Rise of temperature
caused by an abundance
of greenhouse gases in
the atmosphere, which
is the consequence of a
human activity-led,
disturbance of the
natural process in which
a number of gases in the
atmosphere lets the
light of the sun through
and absorbs the
infrared (warmth)
radiation reflected by
the earth and reflects
part of this warmth
back to the earth’s
surface.
Term (German)
Treibhauseffekt
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Kooperationen) sowie
die unterschiedlichen
Administrativen Ebenen
(Bund, Länder,
Genmeinden). Ziel ist es,
Hochwasserrisiken zu
minimieren und der
Entstehung von
Hochwasser
vorzubeugen. (16)
federal states,
municipalities). It aims to
minimise flood risks and
prevent causes of flooding.
Allgemeiner
Temperaturanstieg durch
eine Veränderung der
Atmosphäre. (1)
Overall rise in
temperature caused by a
change of the atmosphere.
Term (English)
Greenhouse gas
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
solar radiation, whereas
the earth’s surface is kept
at a much higher
temperature of, on
average, +14c. An
increase in the
concentration of
greenhouse gases leads to
an increased infrared
opacity of the atmosphere,
and therefore to an
effective radiation into
space from a higher
altitude at a lower
temperature. This causes
a radiative forcing, an
imbalance that can only be
compensated for by an
increase of the
temperature of the
surface-troposphere
system. This is the
‘enhanced greenhouse
effect’.
Greenhouse gases are
those gaseous constituents
of the atmosphere, both
natural and anthropogenic,
that absorb and emit
radiation at specific
wavelengths within the
spectrum of infrared
radiation emitted by the
earth’s surface, the
atmosphere, and clouds.
This property causes the
greenhouse effect. Water
vapour, carbon dioxide,
nitrous oxide, methane,
and ozone are the primary
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
A number of
anthropogically produced
and naturally occurring
gases whose presence in
the atmosphere traps
energy radiated by the
earth. Carbon dioxide is
the most important
greenhouse gas. (2)
Broeikas-gassen
Gassen die bijdragen aan
de opwarming van de
dampkring: kooldioxide
(CO2), methaan (CH4),
lachgas (N2O) en
fluorverbindingen (HFK's,
PFK’s en SF6). (2)(3)(4)
Gases that contribute
to heating up the
earth’s atmosphere:
carbon dioxide (CO2),
methane (CH4), nitrous
oxide (N2O) and a
number of fluoride
compounds (HFK’s,
PFK’s and SF6).
Treibhausgas
Stoffe, die an der
Entstehung des
anthropogen
verursachten
Treibhauseffektes
beteiligt sind. (4)
Substances causing human
induced greenhouse effect.
Term (English)
Groundwater
Habitat
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
greenhouse gases in the
earth’s atmosphere.
Moreover there are a
number of entirely humanmade greenhouse gases in
the atmosphere, such as
the halocarbons and other
chlorine- and brominecontaining substances,
dealt with under the
montreal protocol.
Besides CO2, N2O and
CH4, the Kyoto protocol
deals with the greenhouse
gases sulfur hexafluoride,
hydrofluorocarbons and
perfluorocarbons.
Term not defined
The particular
environment or place
where an organism or
species tend to live; a
more locally circumscribed
portion of the total
environment.
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Groundwater consists of
water that occupies
pores, cavities, cracks
and other spaces in the
crustal rocks. Soil water
is that adhering to the
surface of soil particles
or occupying pore spaces
in between them. (8)
The particular
environment or place
where an organism or
species tends to live; a
more locally
circumscribed portion of
the total environment.
(4)
Grondwater
Water in de grond. (13)
Water below ground
surface.
Grundwasser
Wasserschichten unter
der Erdoberfläche. (1)
Water below ground
surface.
Habitat
Leefgebied van plant- of
diersoort(en). (12)
Living area of plant(s) or
animal(s).
Biotopverbundsyste
m
System von miteinander
in Verbindung stehenden
Biotopen. (4)
System of connected
biotopes.
Term (English)
Heat island
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
An area within an urban
area characterized by
ambient temperatures
higher than those of the
surrounding area because
of the absorption of solar
energy by materials like
asphalt.
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Hitte eiland (term
not widely used)
Een gebied binnen het
stedelijk gebied, welke
gekarakteriseerd wordt
door
omgevingstemperaturen
die hoger zijn dan die van
het omgevende gebied,
als gevolg van de
absorptie van zonneenergie in materialen als
asfalt. (Term translated
from English definition).
(Term translated from
English definition).
Hitzeinsel
Städtische Teilgebiete mit
durchschnittlich höherer
Temperatur, verurscacht
durch
wärmeabsorbierende
Materialien wie z.B.
Asphalt.
An area within an urban
area characterized by
ambient temperatures
higher than those of the
surrounding area because
of the absorption of solar
energy by materials like
asphalt. (IPCC)
Binnendijks
Gebied dat door primaire
waterkeringen wordt
beschermd tegen
overstroming. (10)
De samenhang van het
waterbeleid met andere
beleidsvelden: milieu,
ruimtelijke ordening,
natuur en recreatie. (11)
Area that is protected
from flooding by
primary dams.
Deichhinterland
The integration of
water policy with other
fields of policy:
environment, spatial
planning, nature and
recreation.
Wassermanagemen
t
Area that is situated on
the landside of the primary
dams and is protected
against flooding.
Totality of measures to
manage water systems in a
way that serves common
interests as well as
individual users.
Variabiliteit van klimaat
heft betrekking op de
variaties in the
gemiddelde staat and
andere statistieken van
het klimaat op alle
niveaus in tijd en ruimte,
waarbij naar meer wordt
gekeken dan alleen the
individuele
(Term translated from
English definition).
Natürliche
Klimaschwankungen
Gebiet auf der Landseite
hinterrdem Hauptdeich,
das vor Fluten geschützt
ist.
Gesamtheit der
Maßnahmen, die dazu
dienen, die Gewässer so
zu bewirtschaften, dass
sie dem Wohl der
Allgemeinheit und im
Einklang mit ihm auch
dem Nutzen einzelner
dienen. (4)
Nicht durch den
Menschen verursachte
natürliche
Klimaschwankungen,
verursacht z.B. durch
Vulkanausbrüch u.ä.
Inside the dyke
Term not defined
A term introduced to
describe the zone of
slightly increased air
temperatures that occur
in association with a large
urban area, owing to the
absorption and storage of
solar radiation by the
urban fabric and the heat
generated by the city’s
industries, buildings,
traffic, etc. This can
cause a marked
reduction in the number
of air frosts experienced
annually in the city
centre. (8)
Term not used
Integrated water
management
Term not defined
Term not used
Integraal
waterbeheer
Internal climate
variability
Climate variability refers
to variations in the mean
state and other statistics of
the climate on all temporal
and spatial scales beyond
that of individual weather
events. Variability may be
due to natural internal
processes within the
climate system (internal
The “unforced” natural
changes in climate which
occur on all time and
space scales. (1)
Variabiliteit van
klimaat
Natural climate variability
not caused by man e.g.
volcanic eruptions.
Term (English)
Land use
Landscape
Low emission
building
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
variability), or to variations
in natural or
anthropogenic external
forcing (external
variability).
English definition
Term (Dutch)
The total arrangements,
activities, and inputs
undertaken in a certain
land cover type (a set of
human actions). The
social and economic
purposes for which land is
managed (e.g. grazing,
timber extraction, and
conservation).
Term not defined
The total of
arrangements, activities,
and inputs undertaken in
a certain land cover type
(a set of human actions).
The social and economic
purposes for which land
is managed (for example,
grazing, timber extraction
and conservation). (4)
The total surface form of
any area, rural or urban,
and includes both natural
and man-made features
(both the natural and
cultural landscapes). (8)
Landgebruik en inrichting
Term not defined
Term not used
Laag energie huis
(term not used; see
sustainable building)
Landschap
Definition (Dutch)
weerssituaties.
Variabiliteit kan
veroorzaakt worden
door natuurlijke interne
processen in het
klimaatsysteem (interne
variabiliteit( of door
variaties in natuurlijke of
antropogene externe
druk (externe
variabiliteit). (Term
translated from English
definition).
Het gebruik en de
inrichting van gronden
voor en door natuurlijke,
sociale en economische
functies, waarbij de
gronden niet alleen
bestaan uit het oppervlak,
maar tevens uit de
bodem en het
watersysteem. (22)
De combinatie van het
geheel van ecologische en
historische geografische
structuren (waarin het
samenspel tussen bodem,
water, plantengroei en
landgebruik centraal
staat) en de beleving van
de wijdheid van ruimte.
(11)
Gebouw dat op basis van
haar goede
isolatie/architectuur met
een gering energiegebruik
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Use for natural, social
and economic functions,
where land includes the
soil and water system.
Flächennutzung
Art und Maß der
Beanspruchung von
Grund und Boden. (4)
Type and form of use of
land.
The combination of the
total of ecological and
historical geographical
structures (in which the
relationship between
soil, water, growth of
plants and land use plays
a central role) and the
perception of the
extent of space.
Landschaft,
Kulturlandschaft
Landscape designed by
human beings. There is a
distinction between
landscape close to nature
with a high share of natural
ecosystems and landscape
‘far from nature’ like city
regions and industrial sites.
(Term translated from
German definition).
Niedrigenergiehaus
Vom Menschen gestaltete
Landschaft.
Unterschieden wird
zwischen naturnaher
Kulturlandschaft
(Landschaft mit hohem
Anteil an natürlichen
Ökosystemen) und
naturferner
Kulturlandschaft (Stadt-,
Industrielandschaft,
intensiv genutzte
Agrarlandschaft). (4)
Gebäude die aufgrund
ihrer guten
Isolierung/Architektur
mit geringem
Buildings that can be
heated/cooled with little
energy due to their good
insulation/architecture.
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Meteorology
Term not defined
Mitigation
An anthropogenic
intervention to reduce the
sources or enhance the
sinks of greenhouse gases.
Natural balance
Nature
English definition
Term (Dutch)
The scientific study of the
atmosphere. The term is
usually confined to a study
of the tropospheric and
stratospheric processes,
for these are the layers in
which surface weather is
generated. (8)
Action taken to reduce
the impact of human
activity on the climate
system, primarily through
reducing net greenhouse
gas emissions. (1)
Meteorologie
Term not defined
Term not used
Natuurbalans
Term not defined
A creative and
controlling force in the
universe; the physical
constitution of an
organism; the external
world in its entirety;
natural scenery. (7)
N.b. This term is less
widely used in the English
language, and use tends
to be made of terms such
as habitat, landscape and
biodiversity.
Natuur
Mitigatie
Definition (Dutch)
verwarmd en gekoeld
kan worden. (Term
translated from German
definition).
Leer van de
luchtverschijnselen;
weerkunde. (1)
Het tegengaan en
reduceren van
ontwikkelingen en acties
die klimaatveranderingen
versterken, door het
uitvoeren van beleid en
maatregelen gericht op
onder meer gedrag of
inrichting. (2)(3)
Algehele toestand van
landschap en natuur als
gevolg van veranderingen
die daarin waar te nemen
zijn of hebben
plaatsgevonden. (11)
Het landschap waarin de
mens niet of nauwelijks
heeft ingegrepen,
bestaande uit het geheel
van flora en fauna,
uiteenlopend van grote
tot kleine natuur (van
nationaal park tot
achtertuin) en van
stedelijke tot landelijke
natuur (van stadspark tot
bosgebied). (12)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Energieeinsatz
geheizt/gekühlt werden
können. (6)
Science of weather and
air.
Meteorologie
Wissenschaft des
Wetters. (1)
Science of weather.
The prevention and
reduction of
developments and
actions that enhance
climate change, by
implementing measures
and policies aimed at
behaviour and
design/construction.
General state of the
landscape and nature as
a result of the changes
that have taken place or
can be defined in the
landscape and nature.
The landscape in which
humans have hardly
interfered, consisting of
the total range of flora
and fauna, and from
large-scale to smallscale nature (from
National Park to
backyard) and from
urban to rural nature
(from city park to
forest).
Minderung
Minderung
klimaschädigender
Emissionen. (1)
Make less severe.
Naturhaushalt
Wirkungsgefüge aller
natürlichen Faktoren
(Mineralien, Gesteine,
Boden, Wasser, Luft,
Klima, Pflanzen, Tiere).
(4)
Die physische Welt:
Flora und Fauna,
Landschaft und naturliche
Phanomene im Gegensatz
zu durch den Menschen
gemachten Räumen.
System of all natural
factors (soil, water, air,
climate, animals, plants).
Natur
The physical world,
including plants, animals,
the landscape and natural
phenomena as opposed to
human influence and
human creation. (1)
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
One that would generate
net social benefits whether
or not there is a climate
change. No-regrets
opportunities for
greenhouse gas emissions
reduction are defined as
those options whose
benefits such as reduced
energy costs and reduced
emissions of local/regional
pollutants equal or exceed
their costs to society,
excluding the benefits of
avoided climate change.
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Adaptation options (or
measures) that would be
justified under all
plausible future scenarios,
including the absence of
man-made climate
change. A no regret
option could be one that
is determined to be
worthwhile now (in that
it would yield immediate
economic and
environmental benefits
which exceed its cost),
and continue to be
worthwhile irrespective
of the nature of future
climate. (2)
Geen spijt
(adaptatie) opties
(voor maatregelen)
(term not widely
used)
(Term translated from
English definition).
Term not used
Anpassungsmaßnahmen,
die auch dann
gerechtfertigt wären,
wenn es keinen durch
den Menschen
verursachten
Klimawandel gäbe. Eine
‘no-regret’ Maßnahme ist
wirtschaftlich und
produziert
umgehendsowohl einen
ökonomischen als auch
einen
umweltschutztechnischen
Gewinn, unabhängig von
der zukünftigen
Entwicklung des Klimas.
(Term translated from
English definition).
Adaptation options (or
measures) that would be
justified under all plausible
future scenarios, including
the absence of man-made
climate change. A no
regret option could be one
that is determined to be
worthwhile now (in that it
would yield immediate
economic and
environmental benefits
which exceed its cost), and
continue to be worthwhile
irrespective of the nature
of future climate. (English
definition).
Outside the dyke
Term not defined
Term not used
Buitendijks
Term not defined
The stratosphere
contains a layer in which
the concentration of
ozone is greatest, the socalled ozone layer. This
layer is being depleted by
human emissions of
chlorine and bromine
compounds. (4)
Ozonlaag
Area that is situated on
the sea side of the
primary dams; area is
not protected by
primary dams.
the layer of ozone in
the stratosphere.
Deichvorland
Ozone layer
Adaptatie opties (voor
maatregelen) die
ongeacht of er
klimaatverandering
plaatsvindt, netto sociale
voordelen opleveren.
No-regret mogelijkheden
voor de reductie van
broeikasgas emissies zijn
gedefinieerd als die
opties waarvan de
voordelen, zoals
verlaagde energiekosten
en verminderde emissies
van lokale/regionale
vervuilers,
overeenkomen met of
groter zijn dan de kosten
voor de maatschappij,
met uitzondering van de
voordelen van de
ontweken
klimaatverandering.
(Term translated from
English definition)
Gebied zeewaarts van de
primaire waterkeringen;
gebied wordt niet
beschermd door
waterkeringen. (10)
Laag met zone in de hoge
laag van de dampkring.
(1)(2)
Gebiet auf der Seeseite
vor dem Hauptdeich,
Gebiet das nicht durch
Deich vor Fluten
geschützt ist.
Teil der Stratosphäre in
der die
Ozonkonzentration am
höchsten ist. Durch
Chlor und Brom
Emissionen wird diese
Schicht verbraucht.
Area that is situated on
the seaside of the primary
dams; area is not
protected by primary
dams.
The stratosphere contains
a layer in which the
concentration of ozone is
greatest, the so-called
ozone layer. This layer is
being depleted by human
emissions of chlorine and
bromine compounds.
No regret
(adaptation)
options (or
measures)
Ozonschicht
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Where there are threats
of serious or irreversible
damage, lack of full
scientific certainty shall
not be used as a reason
for postponing costeffective measures to
prevent environmental
degradation. (2)
Principe van
voorzorgsmaatregel
en (term not used)
(Term translated from
English definition).
Vorsorgeprinzip
Eine unsichere
wissenschaftliche
Datenlage darf kein
Grund dafür sein,
kosteneffiziente
Maßnahmen zum Schutz
der Umwelt nicht
durchzuführen, wenn
schwerwiegende und
irreversiebke Schäden zu
erwarten sind.
Where there are threats
of serious or irreversible
damage, lack of full
scientific certainty shall not
be used as a reason for
postponing cost-effective
measures to prevent
environmental
degradation.
Precipitation
Term not defined
Water falling in some
form; rain, snow, sleet
and hail. (1)
Neerslag
Any form of water
falling form the sky:
rain, snow or hail.
Niederschlag
Water falling from the
sky, mainly associated
with rainfalls.
Any form of water falling
from the sky: rain, snow
or hail.
Primary dam
Term not defined
Term not used
Primaire
waterkering
Dam, which, according
to the law on dykes and
dams, offers protection
against high water from
the sea or a big river.
Hauptdeich
Priority area
Term not defined
Term not used
Prioriteitsgebied
Waar er gevaar bestaat
voor serieuze of
onomkeerbare schade,
zal een tekort aan
volledige
wetenschappelijke
zekerheid niet gebruikt
worden als een reden
voor het uitstellen van
kosten-effectieve
maatregelen om
milieubeschadiging te
voorkomen. (Term
translated from English
definition)
Elke vorm van water
welke neerdaalt uit de
lucht: regen, sneeuw,
hagel. (1)
Waterkering die volgens
de wet op de
waterkering bescherming
biedt tegen hoogwater
van zee, ijsselmeer of
grote rivier. (10)
In de ruimtelijke
ordening kunnen
gebieden als
prioriteitsgebieden
gedefinieerd worden,
wanneer locale of
regionale structurele
vereisten dicteren dat
een specifieke functie
prioriteit heeft in dat
gebied. Elke vorm van
planning of actie moet
hiermee rekening
houden. (Term
translated from German
(Term translated from
German definition).
Vorranggebiet
Der Hauptdeich ist das
Kernelement des
Küstenschutzes, er wird
ergänzt durch eine
zweite Deichlinie im Falle
eines Deichbruchs.
Als Vorranggebiete oder
Vorrangsstandorte
können im Rahmen der
Raumordnung Gebiete
oder Standorte festgelegt
werden,
die aufgrund
raumstruktureller
Erfordernisse eine
Aufgabe vorrangig vor
anderen
Aufgaben zu erfüllen
haben (z.B. für die
Erholung, für Natur und
Landschaft, für
The primary dam is the
key element of coastal
protection, it is completed
by a secondary dam,
offering protection in case
of a failing dyke.
Priority areas may be
defined in structural
planning where local or
regional structural
requirements dictate that
a particular function shall
have priority on that area.
Any planning or action
must be compatible with
this priority purpose.
Precautionary
principle
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
definition).
Renewable energy
Term not defined
Restore to nature
Definition (German)
Rohstoffgewinnung, für
Siedlungsentwicklung).
Alle Planungen und
Maßnahmen
müssen mit der
festgelegten vorrangigen
Zweckbestimmung
vereinbar sein. (11)
Energiequellen die sich
durch natürliche
Prozesse regenerieren.
(1)
German definition
translated
Duurzame energie
Energie die niet wordt
opgewekt door de
verbranding van aardolie,
aardgas of steenkool,
maar door schone,
onuitputtelijke bronnen.
(3)(9)
Energy that is taken
from clean, renewable
energy sources.
Nachhaltige
Energiequellen
Term not defined
Those energy sources
which do not rely on
finite reserves of fossil or
nuclear fuels. They
comprise: solar energy,
wind energy, wave
energy, tidal energy,
hydroelectric power and
geothermal energy. (8)
Term not used
Energy sources that are
regenerated by nature.
Reconstructie
Wiederherstellung von
natürlicher,
ursprünglicher Form und
Aussehen eines Objektes.
(4)
Re-establishment of
natural, original forms of
an ecosystem.
Term not defined
Term not used
Retentie-gebied
Reconstruction aims at
strengthening the
quality and
characteristics of
specific landscapes and
natural areas, by using
an integral approach
with regard to the
environment, nature,
landscape, forest land,
recreation and
agriculture.
Area on the landside of
a dyke, that can be used
in periods of high water
to store surplus water.
Renaturierung
Retention area
Überschwemmungsf
lächen
Deichen nachgelagerte
Flächen, die bei extremen
Hochwassern geflutet
werden können. (1)
Area on the landside of a
dyke, that can be used in
periods of high water to
store surplus water.
Risk
Term not defined
A characteristic of a
system or decision where
the probabilities that
certain states or
outcomes have occurred
or may occur are
Risico
Reconstructie heeft
betrekking op het
versterken van de
kwaliteit en
karakteristiek van
specifieke landschappen
en natuurlijke eenheden
door een integrale
aanpak ten aanzien van
milieu, natuur, landschap,
Bos, recreatie en
landbouw. (12)
Binnendijks gebied, dat bij
hoog water gebruikt kan
worden om water
tijdelijk op te vangen.
(10)
Afhankelijk van de
context: ofwel de kans
op schade, ofwel de kans
op schade maal de
omvang van de schade.
(10)
Depending on the
context: either the
chance of damage or
the chance of damage
multiplied by the
dimension of the
Risiken
Gefahren künftiger
Entwicklungen. (1)
Level of danter to future
developments.
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Risk zone
Term not defined
Sea level rise
Term not defined
Sealing
Sectoral planning
English definition
precisely known. Risk is
a combination of the
chance or probability of
an event occurring, and
the impact or
consequence associated
with that event.
Decisions that involve
risk are a special case of
uncertain decisions
where the probabilities
are precisely known. (2)
Term not widely used.
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
damage.
Risicozone
Buitendijkse zone waar
de kans op schade groot
is in vergelijking met
binnendijks gebied. (10)
Zone outside the dyke
in which the chance of
damage is high
compared to the zone
inside the dyke.
Risikozone
Deichvorlandzone in der
die Wahrscheinlichkeit
von Schäden größer ist
als im Deichhinterland.
(Term translated from
Dutch definition).
Zone outside the dyke in
which the chance of
damage is high compared
to the zone inside the
dyke (Dutch definition).
Zeespiegel-stijging
Verhoging van de stand
van het zeewater, als
gevolg van smelten van
ijsvlaktes of toegenomen
regen. (1)
Increase in level of
seawater, due to
melting of ice sheets.
Anstieg des
Meeresspiegels
Langfristiger Anstieg des
Meeresspiegels
verursacht durch
schmelzende Polkappen.
Increase in level of sea
water, due to melting of
ice sheets.
Term not defined
An increase in the mean
level of the ocean.
Eustatic sea-level rise is a
change in global average
sea level brought about by
an alteration to the
volume of the world
ocean. Relative sea-level
rise occurs where there is
a net increase in the level
of the ocean relative to
local land movements. (4)
Term not used
Verharden
Sectorale planning
Bedeckung des Bodens
mit
wasserundurchlässigem
Material wie
Asphalt, Beton u.ä. (11)
Fachplanungen i.w.S. sind
die Planungen und
Maßnahmen die im
Covering the land with a
material impervious to
water, such as asphalt,
concrete, etc.
Term not used
Covering land with
materials like asphalt
and concrete which are
hard for water hard to
penetrate.
Activities from the
different governmental
sectors (especially
Versiegelung
Term not defined
Het bedekken van land
met, voor water niet of
slecht doorlaatbare,
materialen als asfalt en
beton. (22)
Activiteiten bij de
verschillende
overheidssectoren (in het
Fachplanung
Those plans and activities
developed and
implemented by
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Sewer
Term not defined
Spatial planning
Term not defined
English definition
An artificial usually
underground conduit
used to carry off waste
matter, especially,
excrement, from houses,
towns, etc. And surface
water from roads and
paved areas. (8)
Spatial planning goes
beyond traditional land
use planning to bring
together and integrate
policies for the
development and use of
land with other policies
and programmes which
influence the nature of
places and how they
function, including
economic, social and
environmental matters.
Term (Dutch)
Riool
Ruimtelijke planning
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
bijzonder verkeer en
vervoer, milieu, natuur
en water), die erop
gericht zijn te zoeken
naar mogelijkheden om
de ontwikkeling van het
specifieke sectorale
aspect en vaak ook de
ruimtelijke weerslag
daarvan doelmatig te
doen verlopen. (17)
Ondergrondse buis voor
de afvoer van
afvalsoorten,
uitwerpselen e.d. (13)
traffic and transport,
environment, nature
and water) that aim at
searching for
possibilities to develop
the specific sector
aspect and often its
spatial consequences in
a sufficient and
appropriate way.
Drainpipe for the
drainage of waste and
faeces, etc.
Ruimtelijke planning
behelst die activiteiten,
die zijn gericht op het
zoeken van
mogelijkheden om de
ruimtelijke ontwikkeling
vanuit zowel functioneel,
als sociaal, als
economisch, als milieu
oogpunt zo doelmatig te
doen verlopen. (2)
Spatial planning consists
of those activities that
aim at searching for
possibilities to make
sure that spatial
development takes
place in an appropriate
way, both from a
functional, social,
economic and
environmental point of
view.
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Zuständigkeitsbereich
von Bund, Ländern und
Gemeinden durch
Fachstellen zur
Umsetzung ihrer
sektoralen Fachbelange
vorbereitet und
durchgeführt werden.
(11)
departments at federal,
land or local level to meet
their specific
responsibilities.
Abwasserkanal
Kanal zur Ableitung von
Schmutzwasser. (1)
Drainpipe for the drainage
of waste and faeces, etc.
Raumplanung
Zusammenfassende,
überörtliche und
übergeordnete Planung
zur
Ordnung und
Entwicklung eines
Raumes.
Er stellt die langfristigen
und großräumig
bedeutsamen Planungen
und Maßnahmen
zusammenfassend dar
(Bundesraumordnung).
Die Länder
sichern im Rahmen der
Landesplanung die
Verwirklichung der
Grundsätze durch
die Aufstellung von
Programmen und Plänen.
Overall national planning
system that describes the
long-term and spatially
important measures
(bundesraumordnung).
The federal states make
sure, that within the
landesplanung, the aims
are met by developing
programmes and plans.
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Term not used
Zomerbed/
winterbed
Ruimtes waarin het
water van de rivier zich
in de zomer/winter
beweegt. (10)
Space in which the river
water moves in
summer/winter.
Sommerbett
Winterbett
(although term not
used in German)
Space in which the river
water moves in
summer/winter (Dutch
definition).
Sustainable
building
Term not defined
Duurzaam bouwen
Bouwen met bijzondere
aandacht voor
milieukwaliteit en
energiegebruik.
(2)(6)(7)(8)
Building with special
attention to
environmental quality
and energy use.
Nachhaltige
Architektur
Sustainable city
development
Term not defined
Building with special
attention to
environmental quality
(e.g. in terms of building
materials used, water
efficiency features and
energy efficiency
features).
Term not used
Unterschiedliche
Ausdehnung des
Flußbettes in abhänigkeit
von den Jahreszeiten
(Sommer, Winter).
(Term translated from
Dutch definition).
Gebäude, die in
Konstruktion,Materialwa
hl und Unterhalt mit
einem Minimum an
natürlichen Ressourcen
auskommen. Beispiel:
Null Energie Haus.
Duurzame
stedenbouw
Term not defined
Development that meets
the needs of the present
without compromising
the ability of future
generations to meet their
own needs. (4)
Duurzame
ontwikkeling
City development with
special attention for
environmental quality
and energy use.
Development that
provides for the needs
of current generations,
without taking away
possibilities for future
generations to provide
for their needs.
Nachhaltige
Stadtentwicklung
Sustainable
development
Stadtentwicklung unter
der Prämisse von
Umweltfreundlichkeit
und Energieeffizienz.
Innerhalb des
Spielraumes, den die
Natur als
Lebensgrundlage
bereitstellt, ist wirtschaftliche Entwicklung
dauerhaft möglich. (7)
City development that
gives special attention to
environmental quality and
energy use.
Economic development
built on natural capacity.
Urban land use
planning
Term not defined
See spatial planning
Stedelijke
ruimtelijke planning
Stedenbouw met
bijzondere aandacht voor
milieukwaliteit en
energiegebruik. (2)(9)
Een ontwikkeling die
voorziet in de behoefte
van de huidige generatie
zonder daarmee voor
toekomstige generaties
de mogelijkheden in
gevaar te brengen om
ook in hun behoeften te
voorzien. (2)(3)(4)
See spatial planning.
See spatial planning.
Bauleitplanung
Legal procedure within the
authority of local
communities to arrange
urban development.
Voluntary
agreement
Term not defined
An agreement between a
government authority
and one or more private
parties, as well as a
Vrijwillige
overeenkomst
Overeenkomsten tussen
hogere en lagere
overheden of tussen
overheden en private
Commitments between
government authorities
of higher and lower
tiers and between
Selbstverpflichtunge
n
Gesetzlich geregeltes
Verfahren in der
Planungshoheit der
Gemeinden, um die
städtebauliche
Entwicklung
vorausschauend zu
ordnen. (11)(4)
Um gesetzliche
Regelungen zu
verhindern ist die
deutsche Industrie
Summerbed/
winterbed
Nachhaltige
Entwicklung
Buildings that can be
constructed and
maintained with a
minimum of natural
resources e.g. zero
emission houses.
Non legally-binding
regulations e.g. German
industry agreed to a selfcommitment to reduce
Term (English)
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
English definition
Term (Dutch)
unilateral commitment
that is recognised by the
public authority, to
achieve environmental
objectives or to improve
environmental
performance beyond
compliance. (4)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
partijen om op vrijwillige
basis en zonder financiële
vergoeding emissies te
reduceren, een meer
efficiënt energiegebruik
te bevorderen en het
gebruik van duurzame
energiebronnen te
vergroten.
Overeenkomsten zijn
meestal vastgelegd in
convenanten en mja’s
(meerjaren afspraken).
(2)
Het algehele systeem van
waterlopen en
structuren; bestaande uit
zowel oppervlakte- als
grondwater. (13)
government authorities
and private companies
to diminish emissions,
promote a more
efficient use of energy
and enhance the use of
sustainable energy
sources on a voluntary
basis and without
financial compensation.
Agreements are usually
laid down in covenants
and MYA’s (multiple
year agreements).
The total system of
water, waterways and
structures; consisting of
both surface and
groundwater
Polder or association of
polders that form one
administration; the
administration is
responsible for the
quality and quantity of
the water and the dams
and dykes.
A watershed forms the
separation between two
catchments and is
usually formed by the
highest (mountain) ridge
between two
catchments.
Water system
Term not defined
Term not used
Watersysteem
Waterboard
Term not defined
Term not used
Waterschap
Polder of vereniging van
polders onder één
bestuur; bestuur is
verantwoordelijk voor de
kwaliteit en kwantiteit
van het water en de
waterkering. (15)
Watershed
Term not defined
The area of high ground
which separates two
different drainage
systems. (8)
Waterscheiding
Een waterscheiding
vormt een afscheiding
tussen twee
stroomgebieden en
wordt in het algemeen
gevormd door de
hoogste (berg)ruggen
tussen twee
stroomgebieden in. (13)
Term (German)
Wassersystem
(although term not
used in German)
Wasserwirtschaft
(although term not
used in German)
Wasserscheide
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Selbstverpflichtungen zur
CO2 Reduktion
eingegangen. (4)
CO2 emissions.
Wassersysteme in ihrer
Gesamtheit, vom
Grundwasser über das
Oberflächenwasser bis zu
Wasserstrassen.
(Term translated from
Dutch definition).
Administrativer
Zusammenschluß von
Poldern, Verantwortlich
für die Qualität des
Wasser, der Dämme und
Deiche.
(Term translated from
Dutch definition).
Ein Gebiet oder
Gebirgskamm, die
Einzugsgebiete von
Flüssen trennen.
The total system of water,
waterways and structures;
comprising both surface
and groundwater (Dutch
definition).
Polder or association of
polders that form one
administration; the
administration is
responsible for the quality
and quantity of the water
and the dams and dykes
(Dutch definition).
An area or ridge of land
that separates water
flowing to different rivers,
basins or seas. (1)
Term (English)
Watertest
IPPC definition from
glossary of terms used
in the IPCC third
assessment
Term not defined
English definition
Term (Dutch)
Definition (Dutch)
Dutch definition
translated
Term (German)
Definition (German)
German definition
translated
Term not used
Watertoets
De watertoets heeft als
doel om water vanaf het
begin een rol te laten
spelen bij ruimtelijke
plannen en besluiten en
om negatieve effecten en
mogelijke kansen voor
het watersysteem zo
vroeg mogelijk te
signaleren. (10)
The watertest was set
up to let water play a
more important part in
spatial planning and
decisions. The main
aim of the watertest is
to prevent negative
effects of urbanization
and asphalted areas and
make use of chances
the watersytem is
offering for
urbanization.
Wassertes
(although term not
used in German)t
Der Wassertest wurde
eingeführt um dem
Thema Wasser einen
größeren Stellenwerrt in
Entscheidungsprozessen
der Raumordnung zu
geben. Das Hauptziel des
‘watertoets’ ist es,
negative Auswirkungen
von Siedlungen und
versiegelten Flächen
präventive zu verhindern
und die Möglichkeiten,
die das Wassersystem für
die Siedlungsentwicklung
bietet zu nutzen.
(Term translated from
Dutch definition).
The watertest was set up
to let water play a more
important part in spatial
planning and decisions.
The main aim of the
watertest is to prevent
negative effects of
urbanization and asphalted
areas and make use of
chances the watersytem is
offering for urbanization.
(Dutch definition).
REFERENCES:
English sources
(1) Climate Change Scenarios for the United Kingdom: The UKCIP02 Scientific Report April 2002
(2) Climate adaptation Risk, uncertainty and decision-making. UKCIP Technical Report May 2003
(3) Energy White Paper
(4) United Nations Development Programme (2003), Glossary of Climate Change Terminology. Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning.
(5) Venice Group Climate Change Glossary.
(6) International Petroleum Industry Environmental Conservation Association (2001). Climate Change: A Glossary of Terms.
(7) Longman English Dictionary.
(8) Whittow, J. (1984). The Penguin Dictionary of Physical Geography. Penguin Books, London.
Dutch sources
(1) KNMI (2003), The State of the Climate in the Netherlands 2003
(2) Netherlands ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (2001), Fourth National Environment Plan
(3) Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (1999), The Netherlands’ Climate Policy Implementation Plan; Part I: Measures in the Netherlands
(4) RIVM (2000), Environmental Enquiry 2000-2030 (Milieuverkenning 2000-2030)
(5) National government, provinces and water boards (draft), Study on dryness (Droogtestudie)
(6) Stichting Bouwresearch (2003), National Measurepackage Sustainable Building Commercial and Industrial Buildings
(7) Stichting Bouwresearch (2003), National Measurepackage Sustainable Building Ground-, Road- and Waterbuilding
(8) Stichting Bouwresearch (2003), National Measurepackage Sustainable Building Housing
(9) Stichting Bouwresearch (2003), National Measurepackage Sustainable Development
(10) Ministry of Transport, Public Works and Water Management (2000), Third National Coastal Plan
(11) RIVM (2003) Naturbalance 2003 (Natuurbalans 2003)
(12) Netherlands Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Foodquality (2000), National Nature Policyplan, Nature for People, People for Nature
(13) Netherlands Ministry of Transport, Public Works and Water Management (1998), Fourth National Water Plan 1998-2006
(14) RIVM (2004) National Compass Public Health (Nationaal Kompas Volksgezondheid)
(15) www.overheid.nl (or http://www.overheid.nl/guest/aboutgov/government/)
(16) KNMI (2002), Strategy Climateresearch 2002-2006 (Strategie Klimaatonderzoek 2002 – 2006)
(17) Klaassen, A.W. (2000), Spatial policy in theory and practice (Ruimtelijk beleid in theorie en praktijk)
(18) Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality (2003), Climate Change and the functions of the countryside (Klimaatverandering en de functies van het landelijk gebied)
(19) www.vrom.nl
(20) Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (2000), The Netherlands’ Climate Policy Implementation Plan; Part II: Cooperation with foreign countries (NL + EN)
(21) Ministry of Transport, Public Works and Water Management, Policy line Space for the river (Beleidslijn Ruimte voor de rivier)
(22) Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (2004), National Spatial Plan (Nota Ruimte)
German sources
(1) Oxford dictionary 2000
(2) Büntning, Deutsches Wörterbuch 2003
(3) Deutscher Bundestag, Drucksache 14/6529. Paläöklimaforschung in Deutschland –Stand, Ergebnisse, Perspektiven
(4) www.uba.de
(5) DWD, Klimastatusbericht 2002
(6) www.leo.org
(7) UBA, Nachhaltige Entwicklung in Deutschland, 2002
(8) BMVEL 2003, Bericht über den Zustand des Waldes Ergebnisse des forstlichen Umweltmonitorings
(9) WBGU 1998, Strategien zur Bewältigung globaler Umweltrisiken
(10) BUM, 2000 Nationales Klimaschutzprogramm
(11) Glossary of Environmental Terms for Urban and Regional Planners, Federal Environmental Agency 1995
(12) Glossary of the Federal Environmental Agency
(13) Braam, W. (1999), Stadtplanung, Werner Verlag, Düsseldorf
(14) DTV Atlas Stadt (1994), Deutscher Taschenbuchverlag, München
(15) Glossar GLOWA ELBE II. www.glowa-elbe.de
(16) %-Punkte Programm der Bundesregierung: Arbeitsschritte zum verbesserten vorbeugenden Hochwasserschutz
S:\3200\3266 Espace\Documents\Glossary\Appendix 1 - glossary FINAL 26.7.04.doc












