KU Leuven
Supraventriculaire Ritmestoornissen
Prof. Dr. Hein Heidbüchel
Respiratoire Sinusaritmie
KU Leuven
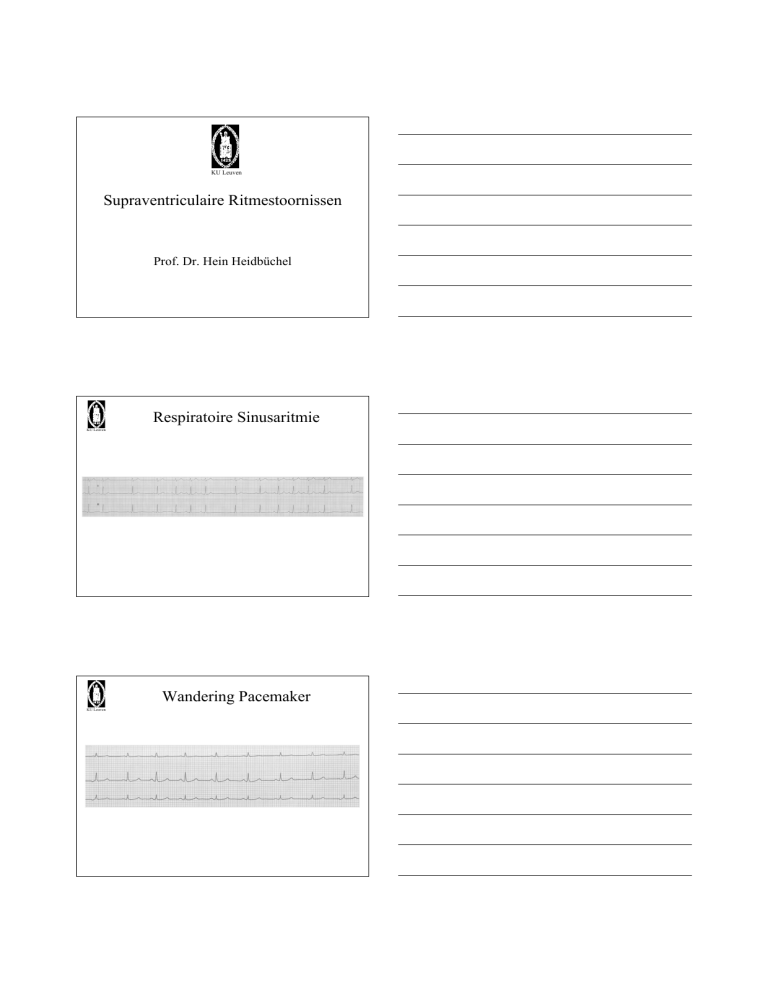
Wandering Pacemaker
KU Leuven
Laag-atriaal ritme
KU Leuven
Sinus Coronarius Ritme
Nodaal Ritme
KU Leuven
Snel nodaal ritme…
KU Leuven
Sinus-arrest of sino-atriaal blok
KU Leuven
Sinus Arrest met Pauze
KU Leuven
Sinus Arrest en Nodale Escape
KU Leuven
Brady-tachy Syndroom
KU Leuven
Mechanismen van Ritmestoornissen /1
Focale mechanismen
KU Leuven
• Mechanismen op het niveau van 1 cel (“focus”)
• Abnormale impuls-vorming
– Automaticiteit
• Normaal, d.i. in cellen met diastolische depolarisatie
sinusknoop > AV knoop > His-Purkinje systeem)
• Abnormaal, d.i. in cellen zonder eigen automaticiteit
myocardiale cel, atriaal of ventriculair
– Getriggerde activititeit
• vroege nadepolarisaties
– “early afterdepolarisations”, EAD
• late nadepolarisaties
– “delayed afterdepolarisations”, DAD
Mechanismen van Ritmestoornissen /2
KU Leuven
Cirkel-activiteit (“reentry”)
• Mechanismen op weefsel-niveau (syncytium)
• Abnormale impuls-geleiding
– Anatomische reentry
• er is een aanwijsbaar circuit
– Functionele reentry
• zonder aanwijsbaar circuit
• d.i. van slag op slag veranderend van ligging.
KU Leuven
Vroege Nadepolarisaties
(“early afterdepolarisations”, EAD)
Oscillaties van de membraanpotentiaal op een (te lang) plateau
bvb. hypokaliëmie, bradycardie, medicatie met QT-verlenging
Late Nadepolarisaties
(“delayed afterdepolarisations”, DAD)
KU Leuven
Oscillaties van de membraanpotentiaal na volledige repolarisatie, door cyclische vrijzetting
van Ca2+ door het sarcoplasmatisch reticulum in een met calcium overladen cel.
De Ca2+-vrijzetting induceert een depolariserende stroom.
bvb. ischemie met reperfusie, digitalis-intoxicatie, ...
Cirkel-aritmieën
KU Leuven
Ontstaan wanneer er unidirectioneel blok optreedt,
met geleiding rondom het blok:
bvb. ventrikel tachycardie na een oud infarct,cirkel-tachycardie bij WPW, ...
Aritmieën: Reentry Circuits … of Foci
EAT
AVRT
AVNRT
IART
Atrial flutter
VT
SART
AF
VT
VF
Voorkamerfibrillatie
“Reeds 15j in voorkamerfibrillatie”
KU Leuven
Voorkamerflutter
Typisch, Type 1
KU Leuven
Flutter: Definitie & Classificatie
KU Leuven
• Definitie: regelmatige atriale activatie (>250/min)
• Indeling gebaseerd op frequentie:
– Type I: 250 tot 340/min
– Type II: 340 tot 430/min
• Indeling gebaseerd op morfologie van de flutter-golven:
– Typische (“common”) flutter: zaagtand in II, III en aVF
– Atypische (“uncommon”) flutter: positieve (dikwijls discrete) P-toppen in
de inferior afleidingen
• In het kader van congenitaal hartlijden en/of na hartchirurgie:
– “intra-atriale reentry tachycardie”, IART (Mustard; ASD; ...)
Flutter: Type 1 (typisch) en 2 (atypisch)
KU Leuven
Paroxysmale SupraVentriculaire Tachycardie
Aritmie Circuits
AVRT
AVNRT
IART
SART
VKF
VT
Voorkamer flutter
VF
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndroom
KU Leuven
Een extra verbinding tussen atrium en ventrikel (“Kent bundel”)
Activatie tijdens sinusritme
Preëxcitatie
KU Leuven
Posteroseptale Kent bundel
Kent Bundel
KU Leuven
Atrium
Endocard
Epicard
Sinus Coronarius
Kransslagader
AV klep
Ventrikel
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndroom
KU Leuven
Orthodrome atrio-ventriculaire reentry
tachycardie (AVRT)
Orthodrome AVRT
Anatomische Localisatie van Kent Bundels
Localisation Algorithm
Based on the polarity of the initial 20 ms of the delta waves (+, -, ±)
KU Leuven
Lead I ± or or V1 R>S
Lead II -
No
No
No
V1 +
Yes
Yes
Yes
Left Free
Wall
CS / MCV
Right Free Wall
aVF +
Septal
aVF -
Yes
RPS
No
Yes
LL
LAL
aVF +
Yes
RA
RAL
aVF ±
Yes LPS
RPS
No
No
No
LP
LPL
II +
Yes
RL
R > S in III
No
No
RP
RPL
MS
Yes
RAS
Adapted from Arruda M. et al., Oklahoma City
Dubbele AV Nodale Fysiologie
KU Leuven
Snelle baan (‘fast pathway’, FP) (fysiologische baan) en
trage baan (‘slow pathway’, SP)
FP
SP
Aritmie Circuits
AVRT
AVNRT
IART
VK flutter
SART
VKF
VT
VF
Slow/Fast AV Nodale Tachycardie
KU Leuven
FP
?
SP
PSVT…
KU Leuven
… gestopt door carotis-massage
KU Leuven
AVNRT: ECG Patterns
KU Leuven
QRS Alternans
KU Leuven
Carotismassage
KU Leuven
Ectopische Atriale Tachycardie
KU Leuven
Localisation of EAT
based on the polarity of the P-wave
KU Leuven
• V1:
– positive
– neg., biphasic or isoelectric
• aVL:
– positive or biphasic
– negative or isoelectric
⇒
⇒
left atrium
right atrium
⇒
⇒
right atrium
left atrium
• Note:
– if V1 = positive and aVL is also positive
(“conflicting”)
⇒ right superior pulmonary vein
⇒ P-wave will be biphasic in V1 during NSR
PJRT
Permanente Junctionele Reentry Tachycardie
