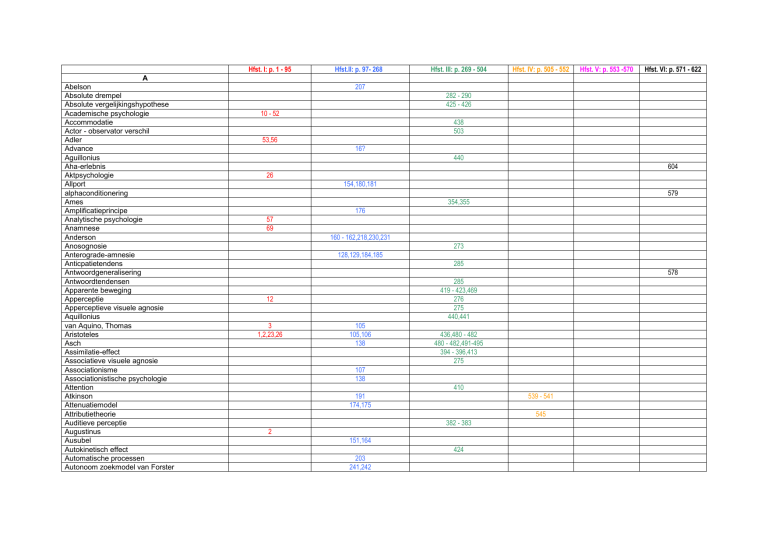
Hfst. I: p. 1 - 95
Hfst.II: p. 97- 268
Hfst. III: p. 269 - 504
Hfst. IV: p. 505 - 552
Hfst. V: p. 553 -570
Hfst. VI: p. 571 - 622
A
Abelson
Absolute drempel
Absolute vergelijkingshypothese
Academische psychologie
Accommodatie
Actor - observator verschil
Adler
Advance
Aguillonius
Aha-erlebnis
Aktpsychologie
Allport
alphaconditionering
Ames
Amplificatieprincipe
Analytische psychologie
Anamnese
Anderson
Anosognosie
Anterograde-amnesie
Anticpatietendens
Antwoordgeneralisering
Antwoordtendensen
Apparente beweging
Apperceptie
Apperceptieve visuele agnosie
Aquillonius
van Aquino, Thomas
Aristoteles
Asch
Assimilatie-effect
Associatieve visuele agnosie
Associationisme
Associationistische psychologie
Attention
Atkinson
Attenuatiemodel
Attributietheorie
Auditieve perceptie
Augustinus
Ausubel
Autokinetisch effect
Automatische processen
Autonoom zoekmodel van Forster
207
282 - 290
425 - 426
10 - 52
438
503
53,56
16?
440
604
26
154,180,181
579
354,355
176
57
69
160 - 162,218,230,231
273
128,129,184,185
285
578
285
419 - 423,469
276
275
440,441
12
3
1,2,23,26
105
105,106
138
436,480 - 482
480 - 482,491-495
394 - 396,413
275
107
138
410
191
174,175
539 - 541
545
382 - 383
2
151,164
424
203
241,242
B
Baddely
Baggett
Ballard
Bartlett
Begin- en eindeffecten
Behaviorisme
Behavioristische motivatietheorie
Bekhterev
Benussi – koffka illusie
Berkowitz
Bernard
Bernheim
Bernouilli
Beschrijvend
Bessel
Biederman
Biological motion perception
Binoculaire parallax
Bleuler
Blum
Blindzien
Body adjustment test
Boring
Boring – figuur
Bottom – up visie
Bower
Braddick
Brady
Braille
Bransford
Breuer
Broadbent
Brown & kulik
Brown – peterson paradigma
Bruner
Bruno
Brunswik
Burtt
C
Cannon
Carmichael
Carpenter
Carpentered world hypothese
Cattel
Causaal/experimenteel onderzoek
30
15
117,194,198
157
115
152 – 154,156,162,191
186
144,146,148
496
493
353
518
18,19
343
75
518
55
294
69
11
158
432
438
385
466
270
383
369
369,469
343 – 348
116,122,123,133
423,424
567
188
159,160
55
167,169,171 – 174,176
126
186,187
413
351,352,446,459,467 – 471
4
78
113
K
518
151
227
400
471
69
555
Causaliteitsprincipe
Centrale kenmerken
Charcot
Cherry
Chomsky
Co – existentie hypothese
Cocktail party effect
Cognitieve dissonantie
Cognitieve neurowy
Cognitieve neurowy (OPKOMST)
Cognitieve processen
Cognitieve psychologie
Cognitieve stijl
Cohort - model van marlsen – wilson
Collins
Common sence psychologie
Compliance
Computationele benadering
Condities ( consistent/conflicterend)
Conditionering
Confusiematrix
Connectionisme
Conrad
Consolidatietheorie
Constantiehypothese
Contention scheduling
Contextafhankelijkheid
Contingent pad
Contasteffect
Conversion
Conway
Cooper
Copernicus
Copernicaanse revoluties
Coren
Corridot – illusie
Covariantieprincipe
Cowan
Craik
Cramer
Crowder
CRT model
D
Dali
Dallenbach
Darwin (C.)
500
492
55
274
410
590
156
410
543,544
266 – 268
48
29,62
144,151 – 166
353,376,495,496
383,384
508
520
243,244
177,214,215,217
245
17,18
500
482,483
345 – 348
364
360
198
40 e.v.
197,198
110
341
207,208
224
542
394 – 396, 413
483
126,127
225
4
4–6
379 – 381
401
500
176
245 – 246,262
294
170,171
228
147
5
357
424
483,490
506
Defensiemechanismen
Delboeuf
Delhaye
Demarest
Denkpsychologie
Denton
Derde gestaltwet
Descartes
Deutsch
Dichotisch luisterexperiment
Dieptepsychologie
Diepterepresentatie
Dieptezicht
Differentiële drempel
Discreet moment
Dispariteit (binoculair/retinaal)
Dixon
Dominantie van het globale
Donders
Dooling
Doornen
Döppler – effect
Dowling
Dubbelbeelden
Dubbelblind experiment
Duncker
Dunlap
Dyade (primair/secundair)
D’Ydewalle
E
Ebbinghaus
Echo
Echoïsch geheugen
EEG
Eerste gestaltwet
Eerste indrukvorming
Efferente kopij
Ehrenstein illusie
Eich
Eidetisch geheugen
Ellis
Elicited response
Emotionele schemata
Episodisch geheugen
Erdelyi
Eriksen
509
294,296 – 298,395,396
247
151
22
357
358,405 – 418
3
108
53
169 – 171
119 e.v., 135
229
413
438
282,283,290 – 293
180 - 181
438,440 – 441
465, 466
363,365
11,36,39
159
144
443
382
441
81
426
464
566
144,246,247,263 – 265
1,23
112,114,135,154
444
169,178
48
350, 360 – 386
491
424
379
254
168,169
619
576
561
224
461,462
ERP
Escher
Ethologie
Etnopsychologie
Event perception
Evolutietheorie/natuurlijke selectie
Equifinaliteit
Exner
Experimentele neurose
Experimentele psychologie
Expliciet geheugen
F
Faciale feedback hypothese
FAN
Favreau
Feature detectors
Feature integration theory
Fechner
Feed – forward
Festinger
Figuur – achtergrond relatie
Figuur – achtergrond wet
Fisher
Fixed interval
Fixed radio
Flashbulb memory
Folkpsychologie
Forster
Fraser illusie
Freud
Functionalistische psychologie
49
355,356,373 – 375
509
8
431
8
59
98
420
579
496
102
560
231
359
343,344,350
350
292 – 294,298 – 299,464
560
543,544
360,361
408,409
375
589
589
125
7
241,242
387,388
6,9,53,55,56
119 e.v., 134,142,182,218
146
507,508
215
Fuzzy – sets
G
Galileo
Ganzfeld
Garcia
Gardner
Gecontroleerde processen
Geheugenpsychologie
Geïnduceerde bewegingen
Geluidsperceptie
Gestaltfactoren
Gestaltkwaliteiten
Gestaltpsychologie
Gevoelens
4
342,343
595,596
202
203
113 – 115,144,154,156
426,427
407
441
27
27
13
108,135,137 – 140,144
341,351,418,420,433,495
Gewaarwording
Gibson
Gilligan
Glucksberg
Göckel
Godden
Goldmeier
Graceful degradation
Gray en wedderburn
Gregory
Grensoverschrijding
H
Hanawalt
Harlow
Hawtorne – effect
Head
Heider
Helmholtz
Hemianopsie
Hemineglect
Hering
Hersenfysiologie
Het geval “John”
Hintzman
Höffding (probleem)
Hogere orde conditionering
Homeostase
Homunculus
Horizontaal – verticaal illusie
Horner
Hubel/wiesel
Hudsonplaten
Hull
Humanistische psychologie
HVI
Hydraulisch model
Hypnose
I
Iconisch geheugen
Identificatie
Illusoire conjunctie
Illusoire dieptedimensie
Indirect/impliciet geheugen
Infantiele amnesie
Informatie – integratie theorie
Informatietheorie
13
99,100
116,122,123
176
279 – 340
359,442,449
1,2
117
409
46
174
399 – 401
158
151
512
79
154
184
499 – 500
340 – 341,441
270
271
441
421
275
218
138
577
518
63
167
390 – 394
541
343,344
400
20,21
57
518 – 520
390 – 394
510
210,212
402
167-169
240
180
102
130,132
379 – 382
469
493
30
547
Informatieverwerkingspsychologie
Informatieverwerkingstheorieën
Inhibitie (proactief/retroactief)
Instincttheorie
Instrumentale conditionering
Integratie van informatie
Intentioneel vergeten
Interactief activatiemodel
Interferentie
Interferentie – effect
Interferentiehypothese
Interindividuele verschillen
Interpositie
Interpretatie
Interstimulus interval
Intraub
Introspectiepsychologie
Inwendig milieu
Ittelson
J
James
Jenkins
Jinfu
Johansson
Johnson
Judd
Juist merkbaar verschil (j. m. v.)
Julesz
Jung
Just
K
Kamin – effect
Kanisza (triangle)
Katona
Kegelmetafoor
Kelley
Kennisrepresentatie
Kepler
Kimble
Klintsch
Koffka
Köhler
Kopfram
Korsakoff
Korte
Kosslyn
63
34
100,138,150,156,162,165 – 265
149
275,363,365,412,416,496
359
506
587
493
123
237
148 – 149
168
213
383 – 386
439
240
420
158
10 e.v.
388,395
550
353
11
358
506,507
553,554
147
390
432 – 434
159, 160
404 – 405
299
441
53,57
227
580,581
379,380
137
194
500,501
212
4
571
221,222
28,29
135,136
341 – 343,358
359
414
101
421,422,424
228 – 230
604
Kulik
Külpe
L
Lachman
Lamarck
Lange
Latent leren
Leerconditie
Leermotivatie en info – verwerking
Leerpsychologie
Leeuwenberg
Levels of processing
Leventhal
Levine
Lewin
Lichtmaskering
Liébault
Lockhart
Loftus
Logisch positivisme
Logogen model van Morton
Lorenz
Lustprincipe
M
Maanillusie
Magnetisme
Magritte
Malmquist
Mandler
Mappingconditie (consistent/gevar.)
Marr
Marrow
Marslen – Wilson
Maslow
Massaro
Maximaliseringsprincipe
Mc Clelland
Mc Dougall
Mc Ginnies
Mc Leod
Mentale rotatie
Mentale scanning
Mere exposure effect
Mesmer
Metafoor van de kathodestraalbuis
Methode van de constante stimuli
125,126
22
159
81
553,554
602 - 603
262 – 265
262 – 265
100
415,416
245 – 265
559
114,154
135,139,140
178
55
145,146
131,154 – 156,209,217
20
242,243
509 – 511
508
450,451
54
357
127
157
202
245
141
243,244
345 – 348
523
167,170,238
244
401
537
506,507
461
197
225 – 228
225
468,469
54
415
286 e.v.
Metzger
Metzler
Michotte
Middeldoelstructuur
Milgram
Milieu interieur
Mill
Miller
Minimum principe
Mitchell
Mnemotechniek
Monteiro
Moray
Morton
Mosovici
MRI
Mowrer
Müller
Müller – Lyer illusie
Münsterberg illusie
Murphy
Murray
Musturbation
N
Na-effecten (figuraal) = nabeelden
Nash
Navon
Necker (cubus)
Negatieve sensatie
Negativiteitseffect
Neisser
Neuronaal spoor
Neuropsychologie
New look psychologie
Newton
Niet-academische psychologie
Niet-contingent pad
Norman
Nuttin
O
O. Hebb
Objectsuperioriteit
Occlusie
Ofsche
Öhman
Omgekeerde T-illusie
441
225
152
428 – 430
61
85,86
518
107,108
61,62
358
155
260 – 262
116,123
174
170,171,176,243
482
50
594
110,111,114
396 – 401,404,405
389
144,154
386
507
537
619
358,359
403,404
363 – 365
366
464
494
64
126,168,178
177
364
352,353,365,376,469
435
53 – 67
542
173,176,205,207,208,220
136,137,143
585,586
110
348,364
439
132
598
390 – 394
Onderscheidingsconditionering
Onmiddellijk geheugen
Ontogenetische prioriteit
Ontwikkelingspsychologie
Oogconvergentie
Operante conditionering
Oppervlakteillusie van Wundt
Opvuleffect
Oriënteertaak
Orlebeke
Orne
Oroniemen
Output interferentie
Ovsiankina
P
Pachauri
Palmer
Pandemoniummodel
Parker
Parmenides
Pars-pro-toto probleem
Patroonmaskering
Pavlov
Pdp-modellen
Pierce & Jastrow
Penfield
Penrose figuren
Perceptie
Perceptuele defensie
Perceptuele illusie
Perceptuele vigilantie
Permanent geheugen
Perserveratietendens
Persoonlijk construct
Persoonlijkheidstheorie
Persoonsperceptie
Perspectief (atmosferisch/lineair)
PET-scans
Phi-fenomeen
Piaget
Pichert
Pilzecker
Plateau
Plato
Plutchik
Poggendorf-illusie
579
184 – 209, 274
360 – 363
165
509
438
393
394
471
263
144
78
407,408
168
140 – 141
144
154 – 156
234
157
105
240 – 245
179
18,19,81
41
471
360
576
464
115,209
373
12
209 e.v.
285
461
351 e.v.
463
274,365
496
495
483 e.v.
440 e.v.
50
420,421,469
131,165,166
160
110,111,114
580
294 – 296,359
2
104,105
566
403 – 405
Pollyannaprincipe
Ponzo-illusie
Pop-outs
Posner
Postman
Pötzl
Pötzleffect
Precedentieprincipe
Pregnantiewetten
Prepardness-hypothese
Prikkelgeneralisering
Primaire bekrachtiger
Priming-effect
Print-now! Mechanisme
Procedureel geheugen
Proefleiderseffect
Propositionele representatie
Pseudoconditionering
Pseudoherinneringen
Pseudo-woorden
Psychoanalyse
Psychofarmacologie
Psychofysica
Psychofysisch parallelisme
Psychogalvanische reactie
Psychogene amnesie
Psychologisch moment
Psychopsychosomatiek
Pygmalioneffect
Q
Quillian
R
Random-punt patronen
Rebound effect of thought suppression
Recovered memories
Redunantie
Referentiekaders
Regressie naar reële objecten
Rehearsal (maintenance/elaborative)
Reiff
Relatieve beweging vgl. hypothese
Relationeel onderzoek
REM-fase
Reminiscentie
Rescorla-Wagner model
Respondant behavior
122
401,402
39
178,179
197
151
352,446,471
465
465
444
405
595
577
494
217
125
102
79
229
579
131,132
237
56
507 – 509
185
114
282 – 300
65
174
127
180
567
82,83
212,214,215,223
441,442
123
127,131 – 133
426,434,435
32
162
446
193
403
425 – 427
69
146 – 148
115
581
576
Retinale dispariteit
Retrograde amnesie
ROC-curve
Rod and Frame test
Rogers
Rorschach
Rosch
Rosenblatt
Rosenthal
Rosenzweig
Rubin
Russisch-motorische school
Ryan
S
Saccadische bewegingen
Sanderparallellogram
SAS (supervisory attentional system)
Schaalillusie
Schachter
Schaduweffecten
Schema
Schematheorie
Schlottman en Shanks
Schumann
Schwartz
Sechenov
Secundaire bekrachtiger
Segmentatie
Segmentatieprobleem
Selectief vergeten
Selfridge
Selisman
Semantisch geheugen
Seriële positie-curve
Shallice
Shepard
Sheriff
Shiffrin
Signaal detectie theorie
Signorelli-probleem
Simon effect
Skinner
Smith
Snelheidscriterium
Sociaal conformisme
Sociale controle
440
128,129,184,185
289
383
57,58
523,524
384,385
216
42
80 – 84
141,142
366,434
355
357
183
394,395
204
413
556,558
440
496
162
430
379,38?
357
594
240
408
142
235
597
102,222 – 225
170,186
205,207,208
225
425
191,202,203
287 – 290
121
472,473
586,587
117,224
239
480 e.v.
482
Sociale hypothese
Socrates
Solomon
Spear
Sperling
Spinoza
Spoorvervaltheorie
Stein
Sternberg
Stevens
Stimulus error
Stroop effect
Structurele informatietheorie
Subceptie
Sublimale perceptie
Sublimatie
Subliminale stimuli
Substitutie hypthese
Subsumption
Succesieve approximations
Suffix-effect
T
Tachistoscoop
Tarr
TAT (+ CAT)
Textuurgradiënten
Theoretische neutraliteit van de prikkel
Thiéry
Thomae
Thomas van Aquino
Thorndike
Tiley
Tinbergen
Titchener
Titchener-cirkels
Tokens
Tolman
Top-down
Top-down effecten
Toren van Hanoi
TOT
TOTE
Transactionalisme
TM (travelling moment)
Treisman
Tulving
362
104 – 106
563 – 565
111
167 – 169,177
566
37 – 39
111
246
199 – 201,241,242
299
14
471 – 473
416,418
463,464
462
508
462 – 464
156
164
596
170,171
360,392,393
447
386
439,449
595
377,401
547
105
584
148
516
13
395
395
30
522
237
237
101,102
212,213
351 – 355
61
353
180,181
169,174,175,179,180
222 – 224, 247
350,413
617
598 – 603
Turing
Turvey
Tweede gestaltswet
Tweede signaalsysteem
W
Wagner
Waite
Wallach
Ward
Watervalillusie
Watson
Weber
Wegner
Weiner
Weiss
Weisstein
Wensvervulling
Wertheimer
Wet van de contiguïteit
Wet van de continuïteit
Wet van de eenvoud
Wet van de gelijkenis
Wet van de gelijkheid
Wet van de nabijheid
Wet van het contrast
Wet van het effect
Wheeler
Wilson
Witkin
Woord- en objectherkenning
Woordfrequentie -effect
Woordsuperioriteitseffect
Wulf
Wundt
Würzburgers
X
Xiaolin
Y
Z
Zaidel
Zaragoza
Zeigarnik
Zeigarnik-effect
Zeigler
Zimbardo
Zintuiglijk geheugen
34
178
364,387 – 405,413
580
63
15 – 19
146
401
359
460
358
485
292
555
123,124
501
567,568
348
508
405,4??
107
410 – 413
413 – 418
107
409,410
407 – 409
107
585,586
116
460
383
1,10 – 13,22,26,27,62
22
234 - …
238
236 – 237
135
108,188,196
276,341,393,394,396-399,471
390
158
155
140 – 143
140 – 143
449
86
167 – 184
274
